Difference between revisions of "Glycerol"
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
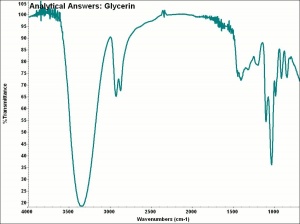
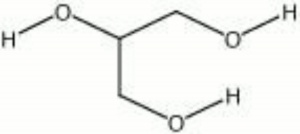
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|aaiGLYCERIN.jpg~FTIR|glycerol.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|aaiGLYCERIN.jpg~FTIR|glycerol.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | ||
| − | |||
== Risks == | == Risks == | ||
Combustible. May explode if mixed with strong oxidizing agents such as chromium trioxide, potassium chlorate or potassium permanganate. | Combustible. May explode if mixed with strong oxidizing agents such as chromium trioxide, potassium chlorate or potassium permanganate. | ||
| − | ThermoFisher: https://www.fishersci.com/store/msds?partNumber=AA4388330&productDescription=GLYCEROL+MONOSTEARATE+PFD+250G&vendorId=VN00024248&countryCode=US&language=en SDS] | + | ThermoFisher: [https://www.fishersci.com/store/msds?partNumber=AA4388330&productDescription=GLYCEROL+MONOSTEARATE+PFD+250G&vendorId=VN00024248&countryCode=US&language=en SDS] |
== Physical and Chemical Properties == | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
Revision as of 14:52, 19 August 2020
Description
A transparent, colorless, viscous liquid that is hygroscopic and has a sweet taste. Glycerol, first isolated in 1779 by Scheele, is a byproduct from the saponification of fats and oils. It is used in the production of alkyd resins, ester gums and dynamite. The thick, neutral liquid is also used as an emulsifier/plasticizer in printing inks, watercolor and gouache paints, glues, cements, and regenerated cellulose (rayon, Cellophane). In some formulations, glycerol is substituted with Sorbitol, or Corn syrup. The term glycerin is used for commercial materials containing more than 95 percent glycerol.
Synonyms and Related Terms
glycerin; glycerine; glycol alcohol; 1,2,3-propanetriol; trihydroxypropane; sweet oil; glyceryl alcohol
Risks
Combustible. May explode if mixed with strong oxidizing agents such as chromium trioxide, potassium chlorate or potassium permanganate.
ThermoFisher: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Miscible with water, ethanol. Insoluble in ether, benzene and chlorinated hydrocarbons.
| Composition | C3H8O3 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 56-81-5 |
| Melting Point | 17.8 |
| Density | 1.2653 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 92.1 |
| Boiling Point | 290 |
Comparisons
Resources and Citations
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: Glycerol. Retrieved June 1, 2003.
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Reed Kay, The Painter's Guide To Studio Methods and Materials, Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1983
- S.R.Trotman, E.R. Trotman, Textile Analysis, J.B. Lippincott Company, Philadelphia, 1932
- Website: conservation termlist : www.hants.org.uk/museums