Difference between revisions of "Nickel yellow"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
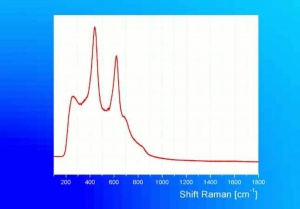
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|nitiyellow632.jpg~Raman]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|nitiyellow632.jpg~Raman]]] | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | R. Mayer, ''The Artist's Handbook of Materials and Techniques'', Viking Press, New York, 1981. | + | * R. Mayer, ''The Artist's Handbook of Materials and Techniques'', Viking Press, New York, 1981. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
* Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000 | * Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000 | ||
Revision as of 15:09, 14 September 2022
Description
A lightfast, bright yellow pigment. Nickel yellow was developed in the 1960s. It is compatible with most types of binding media: gums, glues, oils, waxes, acrylics. The tinting strength of nickel yellow, however, is very low.
Synonyms and Related Terms
nickel-titanium yellow (AAT); nickel titanium yellow; nickel titanate yellow; sun yellow; jaune de nickel (Fr.); Nickeltitangelb (Deut.)
Resources and Citations
- R. Mayer, The Artist's Handbook of Materials and Techniques, Viking Press, New York, 1981.
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000