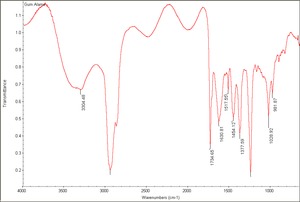
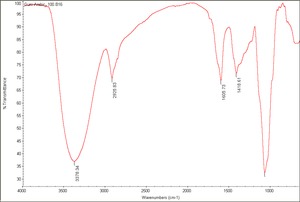
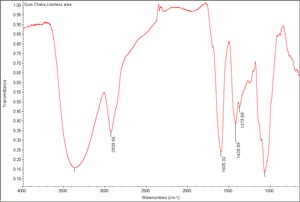
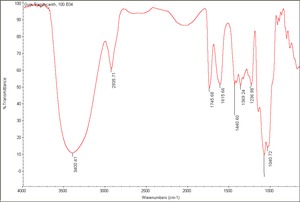
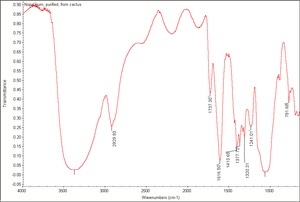
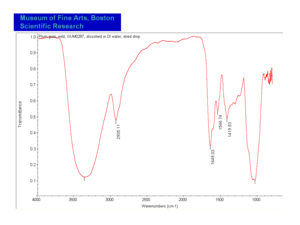
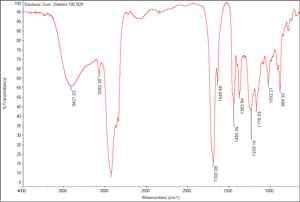
Gum
Description
Carbohydrate containing exudates obtained from some trees or shrubs that are insoluble in alcohol and either soluble or swellable in water. Some gums, such as, agar, funori, and carrageenan, are extracts from seaweed. Gums are used as adhesives, paint binders and sizes. The word 'gum' has also been commonly used to refer to any plant exudate. Examples of natural gums include: gum arabic, gum tragacanth, cherry gum, plum gum, almond gum, balata gum, chicle, damson gum, divul gum, galactan gum, ghatti gum, gum thus, khaya gum, tamarind seed gum, cashew gum, karaya gum, mesquite gum, cholla gum, soap berry gum, tartar gum, tandra gum, orange gum, grapefruit gum, neem gum, sapote gum, drum stick gum, lemon gum, locust bean gum, xanthan gum, seaweed glue, and guar gum.
Synonyms and Related Terms
gums; gomme (Fr.); goma (Esp.); gomma (It); mucilage; plant gums; natural gums
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble or swellable in water. Insoluble in hydrocarbon solvents. May be thickened by the addition of borates, iron salts or alkaline silicates.
| Density | 1.32-1.43 g/ml |
|---|
Resources and Citations
- J. Twilley, The Analysis of Exudate Plant Gums in Their Artisitic Application, Archaeological Chemistry, 357, 1984
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Dictionary of Fiber & Textile Technology (older version called Man-made Fiber and Textile Dictionary, 1965), Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Charlotte NC, 1990
- S.R.Trotman, E.R. Trotman, Textile Analysis, J.B. Lippincott Company, Philadelphia, 1932
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Theodore J. Reinhart, 'Glossary of Terms', Engineered Plastics, ASM International, 1988