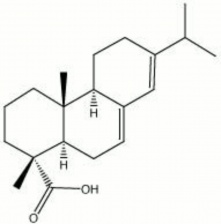
Abietic acid
Description
Yellowish, semi-crystalline powder. Abietic acid is the primary resin acid component of the solid portion (Rosin) of resinous exudations obtained from coniferous trees after the volatiles (turpentine) are removed. Esters of abietic acid, such as methyl abietate, are used in lacquers and varnishes. Resinates of heavy metals, such as lead abietate, are used as driers in oil paints and varnishes. Copper resinate, formed from mixing a copper salt with rosin, is used as a transparent green pigment.
Synonyms and Related Terms
abietinic acid; sylvic acid; 13-isopropylpodocapra-7-13-dien-15-oicacid
Other Properties
Soluble in ethanol, acetone, ether, chloroform and benzene. Insoluble in water.
HLB=8.2 cmc=2 pKa1=6.7
| Composition | C19H29COOH |
|---|---|
| CAS | 514-10-3 |
| Melting Point | 172-175 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 302.45 |
| Refractive Index | optical rotation = -106 |
Hazards and Safety
Combustible. Known contact allergen.
Fisher Scientific: MSDS
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- Richard C. Wolbers, Nanette T. Sterman, Chris Stavroudis, Notes for Workshop on New Methods in the Cleaning of Paintings, J.Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 1990
- The Merck Index, Susan Budavari (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Whitehouse Station, NJ, 12th Edition, 1996 Comment: entry 1
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 615
- Teri Hensick, contributed information, 1998
- MSDS Sheet Comment: Fisher Scientific