Aquamarine
Description
A transparent blue-green Beryl Gemstone. Aquamarines have been mined or gathered as gemstones since the late iron age (500-50 BCE). They are found in Brazil (Minas Gerais, Espirito Santo, Bahia), Siberia, the Urals, Madagascar, Sri Lanka, India, Myanmar, Nigeria (since 1983), Mozambique (since 1991), and the United States (Maine, New Hampshire, Connecticut, North Carolina, Colorado). Aquamarines are composed of a beryllium-aluminum silicate mineral with trace amounts of Iron providing the blue-green color. They are sometimes heat-treated to remove greenish tones. Aquamarines were popular for jewelry in the 19th century. The largest recorded aquamarine was discovered in 1910 and weighed 110 kg (242 pounds). A dark blue beryl, called Maxixe beryl, occurs very rarely naturally and fades in light or heat. The dark blue color is also produced artificially through lengthy irradiation of pink beryl.
Synonyms and Related Terms
blue beryl; axixe beryl (dark blue); akvamarinen (Dan.); Aquamarin (Deut.); aguamarina (Esp.); aigue-marine (Fr.); aquamarijn (Ned.); agua-marinha (Port.)
Physical and Chemical Properties
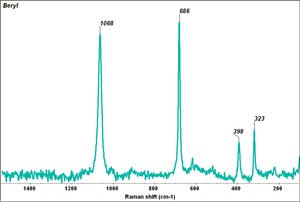
- Hexagonal system with prismatic crystals usually striated lengthwise. Crystals are usually flawless.
- Cleavage is poor in one direction.
- Weakly pleochroic.
- Absorption maxima at 456 and 427 nm.
- Fracture = uneven to conchoidal.
- Luster = vitreous. Streak = colorless.
- Composition = Be3Al2Si6O18
- Mohs Hardness = 7.5 - 8.0
- Density = 2.68-2.71
- Refractive Index = 1.57-1.86
Additional Information
° Michael O'Donoghue and Louise Joyner, Identification of Gemstones, Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2003
Comparisons
Properties of Common Gemstones
Additional Images
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 101
- Sue Fuller, Rocks and Minerals, DK Publishing, Inc., New York City, 1995
- Jack Odgen, Jewellery of the Ancient World, Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "aquamarine" Encyclopædia Britannica [Accessed September 19, 2003].
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aquamarine (Accessed Aug. 30 2005)
- Yasukazu Suwa, Gemstones: Quality and Value, Volume 1, Sekai Bunka Publishing Inc., Tokyo, 1999 Comment: RI=1.577-1.583; Specific gravity=2.72;
- Michael O'Donoghue and Louise Joyner, Identification of Gemstones, Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2003 Comment: RI=1.567-1.590; Specific gravity=2.68-2.80; Abs max=456 and 427 nm