Desert Poplar (Populus euphratica) LC
[[File:|thumb|Yellow Botanic Gardens]]
Description
Desert Poplar (Populus euphratica)is a medium-sized deciduous tree that may grow to a height of about 15 m and a girth of 2.5 m (8.2 ft) where conditions are favourable. The stem is typically bent and forked; old stems have thick, rough, olive-green bark. While the sapwood is white, the heartwood is red, darkening to almost black at the center. The roots spread widely but not deeply. The leaves are highly variable in shape. The flowers are borne as catkins, those of the male are 25–50 mm (0.98–1.97 in) long, those of the female 50–70 mm (2.0–2.8 in). The fruits are ovoid-lanceolate capsules, 7–12 mm (0.28–0.47 in) long, containing tiny seeds enveloped in silky hairs.
The species has a very wide range, occurring naturally from North Africa, across the Middle East and Central Asia to western China. It may be found in dry temperate broadleaf and mixed forests and subtropical dry broadleaf forests at altitudes of up to 4,000 m (2.5 mi) above sea level. Much used as a source of firewood, its forests have largely disappeared or become fragmented over much of its natural range.
Historical importance
The species is used in agroforestry to provide leaves as fodder for livestock, timber and, potentially, fiber for making paper. It is also used in afforestation programs on saline soils in desert regions, and to create windbreaks and check erosion.
Summary of results
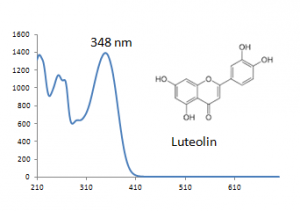
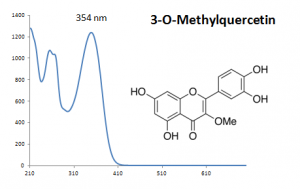
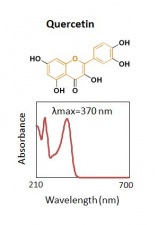
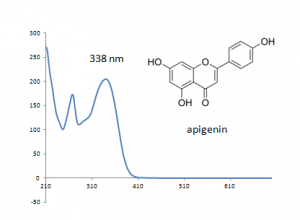
Multiple flavonoids, luteolin, apigenin, chrysoeriol and their glycosides were identified from desert poplar dyed wool samples.
Analytical instrumentation and procedures
Chromatograms
center|frame|Absorbance at 350nm (mAU)
Sample information
Identified compounds
| Compound | RT (min.) | MW | UV/vis | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quercetin | 34.5 | 302 | 372 | Comments here |
| Luteolin | 35.7 | 286 | 348 | |
| 3-O-Methylquercetin | 36.6 | 316 | 358 | |
| Kaempferol | 38.8 | 286 | 366 | |
| Apigenin | 39.2 | 270 | 338 |
References
[1] [2] [3]