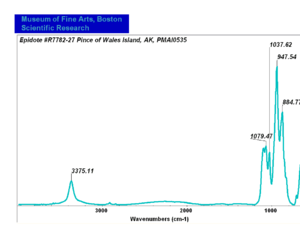
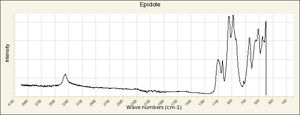
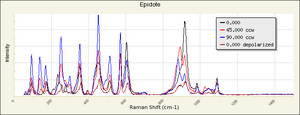
Epidote
Description
A hydrated calcium aluminum iron silicate used occasionally as a Gemstone. Epidote has prismatic shaped crystals that are usually a transparent pistachio green, although its color may vary from a light yellow green to a darker brownish green. Epidote occurs in metamorphic rocks such as gneisses and schists. Notable occurrences have been found in the Urals, Austria, Switzerland, Italy, France, Norway, Mexico, and the United States (Alaska, Idaho, New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Connecticut, Colorado, California).
Synonyms and Related Terms
pistacite; piedmontite (manganese rich); Epidot (Deut.); epidota (Esp.); epidoto (Port.); epidoot (Ned.);
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Slender, prismatic monoclinic crystals with striations.
- Perfect cleavage on one plane.
- Fracture = uneven.
- Luster = vitreous.
- Streak = colorless to gray
| Composition | Ca2(Al, Fe)3(SiO4)3OH |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 6 - 7 |
| Density | 3.3-3.6 g/ml |
| Refractive Index | 1.71 - 1.83 |
Resources and Citations
- Mineralogy Database: Epidote
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Epidote (Accessed Sept. 7, 2005)
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: density=3.25-3.50
- Thomas Gregory, The Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Reinhold Publishing, New York, 3rd ed., 1942
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "epidote" [Accessed December 11, 2001]. (color photo)(tech info)