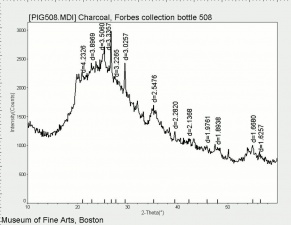
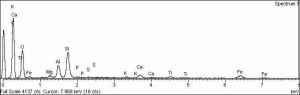
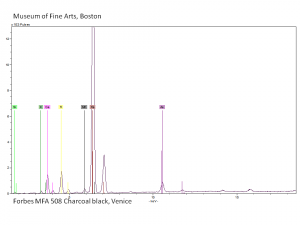
Charcoal
Description
A lightweight, black, porous Carbon containing residue from burned wood (e.g., Willow, Maple, Beech, Linden or plum) or other organic containing materials such as bone, plants or animals. Charcoal contains 80 to 98% carbon with some ash and moisture. Charcoal has been used since ancient times as a drawing material and pigment (see Charcoal black). Charcoal is also sold commercially as a fuel, abrasive, sorbent, filter media, and decolorizer.
See also Activated carbon, Charcoal crayon and Bone black.
Synonyms and Related Terms
trækul (Dan.); negro carbón (Esp.); carbón vegetal (Esp.); Holzkohle (Deut.); charbon de bois (Fr.); karboyno (Gr.); carbonella (It.); carbone (It.); carbo ligni (Lat.); houtskool zwart (Ned.); carvão vegetal (Port.)
Risks
- Fire risk. May ignite spontaneously in air.
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Tiny wood splinters may be visible microscopically.
- Density = oak=0.57; pine=0.28-0.44
- ASTM (1999) lightfastness = I (excellent)
- Refractive Index = opaque
Additional Images
Resources and Citations
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 182
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- R.D. Harley, Artists' Pigments c. 1600-1835, Butterworth Scientific, London, 1982
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Charcoal (Accessed Sept. 2 2005)
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: density for oak=0.57; pine=0.28-0.44
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998