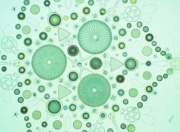
Diatomaceous earth
Description
An absorbent powder composed of the siliceous skeletons of microscopic water plants called diatoms. Diatomaceous earth is composed of 88% [fullrecord.asp?name=silica silica]. The soft, whitish material is used as an inert [fullrecord.asp?name=pigment pigment] or [fullrecord.asp?name=filler filler] in [fullrecord.asp?name=paper paper], [fullrecord.asp?name=paint paint], [fullrecord.asp?name=brick brick], [fullrecord.asp?name=floor tile floor tiles], [fullrecord.asp?name=ceramic ceramics], [fullrecord.asp?name=linoleum linoleum], [fullrecord.asp?name=plastic plastic], [fullrecord.asp?name=soap soap], [fullrecord.asp?name=detergent detergent], and a large number of other products. It reduces [fullrecord.asp?name=gloss gloss], acts as a suspending agent, and increases viscosity. It absorbs dyes well and has been used as a base for lake colors. Diatomaceous earth is also used as an [fullrecord.asp?name=absorbent absorbent], and [fullrecord.asp?name=poultice poultice] since it can absorb up to 4 times its weight of water. Because of its water-absorption capabilities, it is used as a desiccating [fullrecord.asp?name=insecticide insecticide] and is often mixed in formulations with [fullrecord.asp?name=pyrethrins pyrethrins]. Diatomaceous earth has also been used as a decolorizer and filtration aid for purifying [fullrecord.asp?name=oil oils], [fullrecord.asp?name=fat fats], and [fullrecord.asp?name=wax waxes]. Diatomaceous earth has replaced [fullrecord.asp?name=asbestos asbestos] as an [fullrecord.asp?name=insulation insulation] for boilers, blast furnaces, because it is more resistant to shrinkage and does not fail at high temperatures. Other uses include [fullrecord.asp?name=sound insulation sound insulation] and as a very mild [fullrecord.asp?name=abrasive abrasive] in metal [fullrecord.asp?name=polish (material) polishes] and toothpaste.
Synonyms and Related Terms
diatomite; poudre de diatomes (Fr.); tierra de diatomeas (Esp.); diatomito (Port.); Diatomeenerde, Kieselgur (Deut.); diatomenaarde (Ned.); Celite [Celite]; infusorial earth; kieselguhr; fossil flour; tripolite; Sil-O-Cel; diatomaceous silica; siliceous earth; Super-Cel; Kenite; Diactiv; Primisil;
Other Properties
Soluble in alkalis. Insoluble in acids except HF.
| Density | 1.9-2.35 |
|---|---|
| Refractive Index | 1.435 |
Hazards and Safety
Inhalation of dust may cause silicosis. Noncombustible.
Comparisons
Properties of Common Abrasives
Authority
- The Dictionary of Paper, American Paper Institute, New York, Fourth Edition, 1980
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966 Comment: density 2.31 and ref.index.1.435
- Ralph Mayer, Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- G.S.Brady, G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p.266
- Reed Kay, Reed Kay, The Painter's Guide To Studio Methods and Materials, Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1983
- Michael McCann, Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- J. Dawson, J. Dawson, 'Solving Museum Insect Problems: Chemical Control' , CCI Technical Bulletin, Candian Conservation Institute, Ottawa, No. 15
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000