Arylide
Description
A class of synthetic yellow, orange and red organic colorants. These insoluble direct azo dyes were first synthesized from aniline-based diazonium salts and acetoacetarylide in 1909. Arylide was sold commercially as Hansa yellow by Hoechst AG in 1915. Arylide yellows have good tinting strength, opacity and solvent resistance. They have good lightfastness and are primarily used in printing inks, plastic, rubbers, as well as architectural and artists paints. Monoarylide yellows have better lightfastness than diarylides.
Synonyms and Related Terms
monoarylide; diarylide; azo dye; monoazo dye; Hansa yellow; colorante azoico (Esp.); colorante azoico (It.)
Comparisons
| Pigment number | Manufacture | Pigment name | Manufacture CI number | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
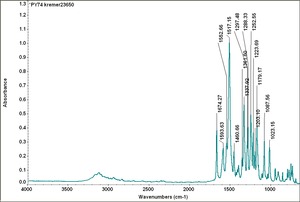
| PY074 | Kremer | |||
| PY001 | Sun | arylide yellow | 272-0008 | |
| PY003 | Sun | arylide yellow | 272-3119 |
Other Properties
Most arylide dyes are soluble in organic solvents. Resistant to water, oil, acids and bases.
| Melting Point | 150 (dec) |
|---|
Hazards and Safety
May bleed in paints. Decomposes at temperatures over 150 C.
Potential carcinogen.
Additional Information
B.Berrie, S.Q.Lomax, "Azo Pigments: Their History, Synthesis, Properties and Use in Artists' Materials" in Studies in the History of Art, No.57, National Gallery of Art, Washington DC, 1997.
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- B. Berrie, S.Q. Lomax, 'Azo Pigments: Their History, Synthesis, Properties and Use in Artists' Materials', Studies in the History of Art , National Gallery of Art, Washington DC, No. 57, 1997
- Website address 1 Comment: www.handprint.com