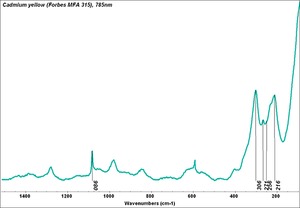
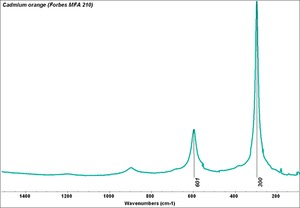
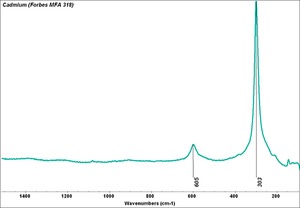
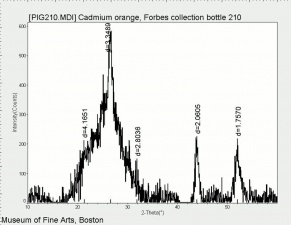
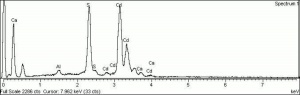
Cadmium sulfide
Description
Cadmium sulfide and cadmium sulfoselenide are intense colorants ranging in color from bright yellow to deep red. Cadmium sulfide was first synthesized in Germany in 1817 and later marketed as an artist pigment in the mid 19th century. Its use was not widespread, however, until about 1917. The finely divided, stable, light resistant particles are deeply colored. Early preparations of cadmium pigments had widely varying particles sizes from 0.1 to 7 micrometers, while recently manufactured pigments contain only submicrometer particles. Since the pure pigment was expensive, cadmium pigments were also sold in diluted lithopone mixtures called cadmopones starting in 1927. Currently, cadmium pigments are primarily used in plastics, ceramics, metal enamel coatings, and as glass colorants. They are permanent and have good hiding power.
See also Cadmium yellow and Cadmium red.
Note: Cadmium sulfide also occurs naturally in the minerals greenockite and hawleyite.
Synonyms and Related Terms
cadmium yellow (PY 37); cadmium red (PR 108); cadmium brown; cadmium orange (PO 20); CI 77199; CI 77202; Cadmiumgelb (Deut.); Cadmiumsulfid (Deut.); sulfure de cadmium (Fr.); sulfuro de cadmio (Esp.); theioycho kadmio (Gr.); solfuro di cadmio (arancio di cadmio) (It.); cadmiumoranje (Ned.); sulfureto de cádmio (Port.); cadmium monosulfide; greenockite (mineral); hawleyite (mineral); jaune brilliant; cadmopone
Risks
Toxic by ingestion and inhalation. Carcinogen.
ThermoFisher: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Cubic or hexagonal crystals. Soluble in concentrated mineral acids with the evolution of H2S. Insoluble in water. May fluorecse red.
Particles are tiny (about 1 micrometer) and have a high refractive index.
| Composition | CdS |
|---|---|
| CAS | 1306-23-6 |
| Melting Point | sublimes at 980 C |
| Density | 4.35-4.82 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 144.5 |
| Refractive Index | e=2.506, w=2.529 |
Resources and Citations
- I. Fiedler, M. Bayard, "Cadmium yellows, oranges and reds", Artists Pigments, Volume 1, R. Feller (ed.), Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 1986.
- Nicholas Eastaugh, Valentine Walsh, Tracey Chaplin, Ruth Siddall, Pigment Compendium, Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2004
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- The Dictionary of Art, Grove's Dictionaries Inc., New York, 1996 Comment: "Pigment"
- Reed Kay, The Painter's Guide To Studio Methods and Materials, Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1983
- R.D. Harley, Artists' Pigments c. 1600-1835, Butterworth Scientific, London, 1982
- Monona Rossol, The Artist's Complete Health and Safety Guide, Allworth Press, New York, 1994
- Book and Paper Group, Paper Conservation Catalog, AIC, 1984, 1989