Difference between revisions of "Calcium hypochlorite"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
A white, crystalline solid. Calcium hypochlorite is a strong oxidizing [[bleaching agent|bleach]]. It has been used in weak concentrations (0.5%) to bleach [[textile|textiles]] and [[paper]] although it may leave traces or residual chloride. It is also used as a [[bactericide]], [[fungicide]], and [[disinfectant]]. | A white, crystalline solid. Calcium hypochlorite is a strong oxidizing [[bleaching agent|bleach]]. It has been used in weak concentrations (0.5%) to bleach [[textile|textiles]] and [[paper]] although it may leave traces or residual chloride. It is also used as a [[bactericide]], [[fungicide]], and [[disinfectant]]. | ||
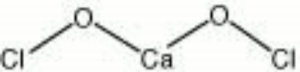
| − | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|calcium hypochlorite.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
calcium hypochloride; bleaching powder; chloride of lime; calcium oxychloride; calcium salt of hypochlorous acid; Losantin; chlorinated lime | calcium hypochloride; bleaching powder; chloride of lime; calcium oxychloride; calcium salt of hypochlorous acid; Losantin; chlorinated lime | ||
| − | [ | + | ==Risks== |
| + | |||
| + | * Toxic chlorine gas may form when mixed with acids or ammonia. | ||
| + | * Fire risk in contact with organic materials. | ||
| + | * Severely corrosive to skin tissue on contact, inhalation, or ingestion. | ||
| + | * The presence of trace heavy metals or their salts can accelerate oxidation. | ||
| + | * Flinn Scientific: [https://www.flinnsci.com/sds_200-calcium-hypochlorite/sds_200/ SDS] | ||
| − | == | + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == |
Decomposes in water and ethanol. | Decomposes in water and ethanol. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 28: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 2.35 | + | | 2.35 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ||
| Line 28: | Line 34: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | == Resources and Citations == |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | * ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | ||
Latest revision as of 14:13, 18 May 2022
Description
A white, crystalline solid. Calcium hypochlorite is a strong oxidizing bleach. It has been used in weak concentrations (0.5%) to bleach textiles and Paper although it may leave traces or residual chloride. It is also used as a Bactericide, Fungicide, and Disinfectant.
Synonyms and Related Terms
calcium hypochloride; bleaching powder; chloride of lime; calcium oxychloride; calcium salt of hypochlorous acid; Losantin; chlorinated lime
Risks
- Toxic chlorine gas may form when mixed with acids or ammonia.
- Fire risk in contact with organic materials.
- Severely corrosive to skin tissue on contact, inhalation, or ingestion.
- The presence of trace heavy metals or their salts can accelerate oxidation.
- Flinn Scientific: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Decomposes in water and ethanol.
| Composition | Ca(OCl)2 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 7778-54-3 |
| Density | 2.35 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 142.98 |
Resources and Citations
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Thomas Gregory, The Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Reinhold Publishing, New York, 3rd ed., 1942
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Pam Hatchfield, Pollutants in the Museum Environment, Archetype Press, London, 2002
- Book and Paper Group, Paper Conservation Catalog, AIC, 1984, 1989
- Hermann Kuhn, Conservation and Restoration of Works of Art and Antiquities, Butterworths, London, 1986
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 1648