Difference between revisions of "Category:Flavonoids: Ukiyo-e colorant"
| (35 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:SC359574.jpg|right|400px|link=Kiyomitsu I, Yoritomo's Hunt at the Foot of Mount Fuji, 11.19694|Yoritomo's Hunt by Torii Kiyomitsu I]] |
| − | <font size="3">'''[[Flavonoid|Flavonoids]]'''</font>: A group of organic | + | <font size="3">'''[[Flavonoid|Flavonoids]]'''</font> フラボノイド: A group of organic colorant composed of heterocyclic aromatic compounds. For this database, a group of organic yellow colorants have been grouped under flavonoids due to this common chemical composition and difficulty in identifying them individually. Organic yellow colorants that have been thought to have been traditionally used in ukiyo-e prints that fall into this category are: Gardenia (''Gardenia jasminoides'') or (梔子 ''kuchinashi''), ''Miscanthus tinctorius'' or (苅安 ''kariyasu''), Chinese bayberry (''Myrica rubra'') or (山桃 ''yamamomo''), Japanese pagoda tree (''Styphnolobium japonicum'') or (槐 ''enju''), and Toringo crabapple (''Malus toringo'') or (棠梨 ''zumi''). |
| − | + | Flavonoids have been detected throughout the production of prints from 1690s through the 1860s. With current non-destructive analytical techniques, it is difficult to identify the exact source of each flavonoid. Flavonoids are duller and more beige when compared to the vibrant yellows produced by [[:Category:Turmeric: Ukiyo-e colorant|turmeric]] and [[:Category:Orpiment: Ukiyo-e colorant|orpiment]]. On prints, the dull appearance of flavonoids is little known since it can be their natural state or due to age and/or fading. | |
| − | '''For | + | '''For additional information see:''' [[Flavonoid]], [[Gardenia]], [[Gardenia LC]], [[Kariyasu]], [[Chinese grass (Miscanthus tinctorius) LC]], [[Pagoda tree]], [[Pagoda tree (Styphnolobium japonicum) LC]], [[Zumi]] |
| + | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 43: | Line 44: | ||
== Analysis == | == Analysis == | ||
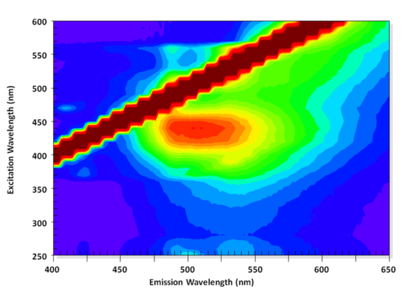
| − | + | Flavonoids, such as the Japanese pagoda tree (''enju'') and ''Miscanthus tinctorius'' (''kariyasu'') fluoresce weakly under ultraviolet radiation and have some differences in their EEM patterns. At this point, however, due to the difficulty in distinguishing these organic yellows, the decision was made to group them as flavonoids to minimize mistakes in identification. | |
<gallery mode="packed" heights="200px" style="text-align:left;"> | <gallery mode="packed" heights="200px" style="text-align:left;"> | ||
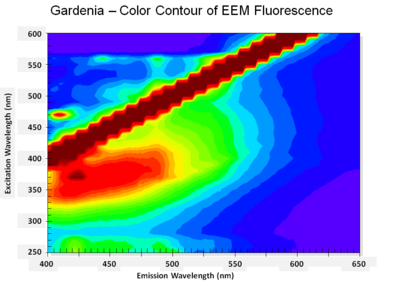
| − | + | Gardenia color.PNG|<center>3D EEM plot for Gardenia (''kuchinashi'')</center> | |
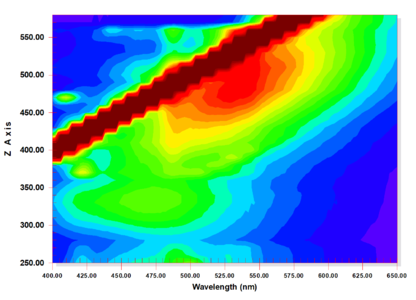
| + | Kariyasu color.png|<center>3D EEM plot for ''Miscanthus tinctorius'' (''kariyasu'')</center> | ||
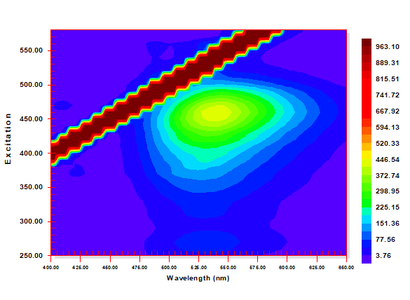
| + | Mountain peach color.png|<center>3D EEM plot for Chinese bayberry (''yamamomo'')</center> | ||
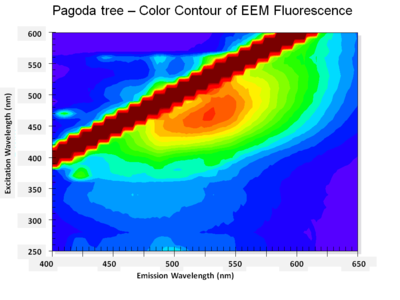
| + | Pagoda tree color.PNG|<center>3D EEM plot for Japanese pagoda tree (''enju'')</center> | ||
| + | Toringo crabapple color.png|<center>3D EEM plot for Toringo crabapple (''zumi'')</center> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| − | == | + | ==Images of Flavonoids== |
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
| − | kuchinasi gardenia grp.jpg| | + | kuchinasi gardenia grp.jpg|Gardenia fruit (''kuchinashi'') |
| − | File:gardenia_dyed paper.jpg| | + | File:gardenia_dyed paper.jpg|Paper dyed with gardenia |
| − | File:kariyasu_pieces.jpg| | + | File:kariyasu_pieces.jpg|''Miscanthus tinctorius'' (''kariyasu'') |
| − | File:Pagoda tree buds.JPG| | + | File:Pagoda tree buds.JPG|Japanese pagoda tree buds (''enju'') |
| − | File:pagoda tree_dyed paper.jpg| | + | File:pagoda tree_dyed paper.jpg|Paper dyed with Japanese pagoda tree |
| + | File:NMAH-AHB2017q005552.jpg|Extract of zumi, <small>by National Museum of American History</small>|link=https://americanhistory.si.edu/collections/nmah_1323753 | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Take photos of the other yellows to add. | ||
==List of Prints == | ==List of Prints == | ||
| − | + | Below is a list of prints where flavonoids were detected. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 22:13, 8 April 2024
Flavonoids フラボノイド: A group of organic colorant composed of heterocyclic aromatic compounds. For this database, a group of organic yellow colorants have been grouped under flavonoids due to this common chemical composition and difficulty in identifying them individually. Organic yellow colorants that have been thought to have been traditionally used in ukiyo-e prints that fall into this category are: Gardenia (Gardenia jasminoides) or (梔子 kuchinashi), Miscanthus tinctorius or (苅安 kariyasu), Chinese bayberry (Myrica rubra) or (山桃 yamamomo), Japanese pagoda tree (Styphnolobium japonicum) or (槐 enju), and Toringo crabapple (Malus toringo) or (棠梨 zumi).
Flavonoids have been detected throughout the production of prints from 1690s through the 1860s. With current non-destructive analytical techniques, it is difficult to identify the exact source of each flavonoid. Flavonoids are duller and more beige when compared to the vibrant yellows produced by turmeric and orpiment. On prints, the dull appearance of flavonoids is little known since it can be their natural state or due to age and/or fading.
For additional information see: Flavonoid, Gardenia, Gardenia LC, Kariyasu, Chinese grass (Miscanthus tinctorius) LC, Pagoda tree, Pagoda tree (Styphnolobium japonicum) LC, Zumi
Examples of Flavonoids in Ukiyo-e Prints
|

|

|

|

|
Analysis
Flavonoids, such as the Japanese pagoda tree (enju) and Miscanthus tinctorius (kariyasu) fluoresce weakly under ultraviolet radiation and have some differences in their EEM patterns. At this point, however, due to the difficulty in distinguishing these organic yellows, the decision was made to group them as flavonoids to minimize mistakes in identification.
Images of Flavonoids
Take photos of the other yellows to add.
List of Prints
Below is a list of prints where flavonoids were detected.
Pages in category "Flavonoids: Ukiyo-e colorant"
The following 51 pages are in this category, out of 51 total.
B
E
- Eisen, Kawasaki, No. 3 from an untitled series of the Fifty-three Stations of the Tôkaidô Road, 11.25617
- Eisen, Minazuru-hime as Ono no Komachi and Benkei as Kisen Hôshi, from the series Characters from the Life of Ushiwaka as the Six Poetic Immortals, 11.25669
- Eisen, The Song Evening Mist at Asama Peak, on Scrap-paper Fabric with an Itchû-bushi Libretto, from the series A Modern Pine Needle Collection, 11.17878
- Eishi, Shizuka of the Shizutamaya, from the series Beauties of the Yoshiwara as Six Floral Immortals, 53.21
- Eizan, Kashiku of the Tsuruya, from the series Array of Beauties of the Pleasure Quarters, 11.17716
F
H
- Harunobu, A Young Woman in a Summer Shower, 11.19430
- Harunobu, Courtesan and Kamuro Looking at the Face of a Komusô Reflected in a Mirror, 45.833
- Harunobu, Courtesan Reading a Letter by Moonlight Reflected on Snow; Parody of Son Kang, 11.19438
- Harunobu, Courtesan Riding a Carp and Reading a Letter; Parody of the Immortal Qin Gao, 06.969
- Harunobu, Courtesan Watching Two Kamuro Make a Snow Dog, 21.4463
- Harunobu, Kojima Bingo no Saburô Takanori, 11.19633
- Harunobu, Osen of the Kagiya and a Young Man with a Cat, 11.19496
- Harunobu, Parody of Saigyô Hôshi: Courtesan Looking at a Screen Painting of Mount Fuji, 11.19431
- Harunobu, Poem by Saigyô Hôshi, from an untitled series of Three Evening Poems, 34.348
- Harunobu, The Sake Cup, sheet 4 of the series Marriage in Brocade Prints, the Carriage of the Virtuous Woman, known as the Marriage series, 11.19475
- Hiroshige I, Naitô Shinjuku, Yotsuya, from the series One Hundred Famous Views of Edo, 11.35823
- Hokkei, Goat Standing by a Plum Tree, 21.9277
- Hokkei, Ômori, from the series Souvenirs of Enoshima, a Set of Sixteen, 11.19845
K
- Kiyomasu I, Courtesan Reading a Poem, 28.198
- Kiyomasu II, Actors Segawa Kikunojô I as Yomogiu, Ichikawa Ebizô II as Tono no Hyôe, and Yamamoto Kyôzô as Kureha, 21.5459
- Kiyomasu II, Actors Ôtani Hiroji II as Washi no Chôkichi and Arashi Tominosuke as Tarui Osen, 21.5458
- Kiyomitsu I, Actor Ichikawa Yaozô I as Soga no Gorô Tokimune, 06.401
- Kiyomitsu I, Actor Segawa Kikunojô II as Itsuki, 11.19020
- Kiyomitsu I, Actor Segawa Kikunojô II as Seryômura Okiku, 11.18992
- Kiyomitsu I, Yoritomo's Hunt at the Foot of Mount Fuji, 11.19694
- Kiyonaga, The Brine Maidens, from the series Current Manners in Eastern Brocade, 11.13880
- Kokan, Couple Cooling Off on a Garden Bench, 11.19524
- Koryusai, Descending Geese at Mimeguri, from the series Fashionable Eight Views of Edo, 11.14627
- Kunisada, Poem by Ariwara no Narihira Ason: (Actor Ichikawa Danjûrô VIII as) Seigen, from the series Comparisons for Thirty-six Selected Poems, 11.42663
- Kunisada, Young Woman Pointing and Giggling, from the series Types of the Floating World Seen through a Physiognomist's Glass, 34.471
- Kuniyoshi, Actor Ichikawa Kodanji IV as the Ghost of Asakura Tôgo, 11.30460
- Kuniyoshi, Takeout Sushi Suggesting Ataka, from the series Women in Benkei-checked Fabrics, 11.36360
- Kuniyoshi, Tsumagome: Abe no Yasuna and the Fox Kuzunoha, from the series Sixty-nine Stations of the Kisokaidô Road, 11.41803
M
S
- Sharaku, Actor Osagawa Tsuneyo II as Ippei's Older Sister Osan, 11.14673
- Sharaku, Actor Osagawa Tsuneyo II as Ippei's Older Sister Osan, 11.14674
- Sharaku, Actor Osagawa Tsuneyo II as Ippei's Older Sister Osan, 21.7244
- Shinsai, Chapters 25–27, from the series The Tale of Genji, 21.9264
- Shunshō, Actor Segawa Kikunojô III as Shirokiya Okoma, from the series Fans of the East, 11.14871
- Shunshō, No. 6, Cui Zongzhi (Saisôshi), from the series Eight Immortals of The Wine Cup, 11.14847
T
- Toshinobu, Actors Matsushima Hyôtarô as the Courtesan Senzai and Nakamura Ujûrô and Nanboku Magotarô as Samurai, 11.13225
- Toyoharu, A Fashionable Picture of Wada's Banquet, from the series Scenes of Japan in Perspective Pictures, 54.1499
- Toyokuni, Actor Arashi Kitsusaburô I as the Monkey Trainer Yojirô, in the Horikawa Scene of the Play Oshun and Denbei, 11.30331