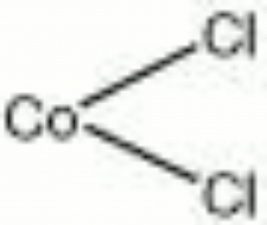
Cobaltous chloride
Description
Pale blue, flaky crystals. Cobaltous chloride is most commonly used as a color indicator of moisture. On exposure to moist air, anhydrous cobaltous chloride absorbs water forming pink-color hexahydrate crystals. The blue anhydrous form can be regenerated by heating at 52-56 C. Cobaltous chloride is added to silica gel and activated alumina type desiccant as a moisture indicator. It has also been used in indicator paper.
Synonyms and Related Terms
cobalt chloride; cobalt dichloride; cobalt (II) chloride; Cobalt(II)-chlorid (Deut.)
Other Properties
Soluble in water, alcohols, acetone, ether, glycerol, pyridine.
| Composition | CoCl2 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 7646-79-9 |
| Melting Point | 735 |
| Density | 3.348 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 129.84 |
| Boiling Point | 1049 |
Hazards and Safety
Suspected carcinogen. Skin contact may cause allergies, especially on elbows, neck and ankles. Chronic inhalation may cause asthma. Ingestion may cause vomiting, diarrhea and the sensation of hotness.
Mallinckrodt Baker: MSDS
Additional Images
Authority
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 406
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The Dictionary of Paper, American Paper Institute, New York, Fourth Edition, 1980
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 2498
- Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cobalt_chloride (Accessed Jan. 15, 2006)
- B. Gascoigne, How to Identify Prints, Thames & Hudson, London, 2004
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: ref. index=