Lanital
Description
[Snia Viscosa] A trademark for the first commercially manufactured regenerated Protein fiber. In the early 1930s, an Italian chemist, Antonio Ferretti developed a successful method to make regenerated protein fibers. Lanital was patented in 1935 and sold in 1936. Lanital is made from Casein. Casein is processed with Formaldehyde or Benzaldehyde and metal salts then pressed through spinnerets to form long, silk-like fibers. Casein fibers are softer and smoother than Wool and contain less Sulfur. They are not susceptible to moths but can be degraded by some bacteria. Casein fibers are usually cream colored and they accept dyes well but have poor washfastness. Most often casein fibers are blended with wool in fabrics and hat felts. Lanital, along with other regenerated protein fibers, have been replaced by other synthetic fibers, because casein fibers are weak when wet and susceptible to microbiological growths.
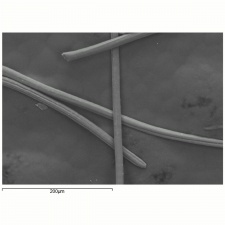
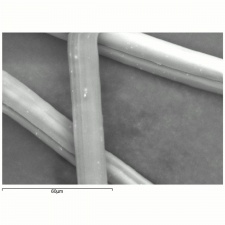
See also photomicrographs at Lanital fibers in Fiber Reference Image Library.
Synonyms and Related Terms
Lanitol (sp)
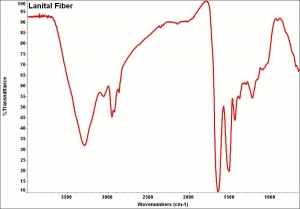
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Insoluble in dilute acids, hydrogen peroxide and most organic solvents. Affected by alkalis.
- Filaments are smooth.
- Cross sections = circular, bean-shaped.
| Density | 1.25-1.3 |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 20-30 micrometers |
| Tenacity | 0.9-1.1 g/denier (dry); 0.3-0.6 (wet) |
| Elongation | 60-70% |
| Moisture regain | 14% |
Comparisons
Properties of Synthetic Fibers
Resources and Citations
- Joan Kiplinger 'Vintage Fabrics' at Fabrics.net
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 153
- Rosalie Rosso King, Textile Identification, Conservation, and Preservation, Noyes Publications, Park Ridge, NJ, 1985
- Marjory L. Joseph, Introductory Textile Science, Holt, Rinehart and Winston, Fort Worth, TX, 1986
- J.Gordon Cook, Handbook of Textile Fibres:II Man-made Fibres, Merrow Publishing Co. , Durham, England