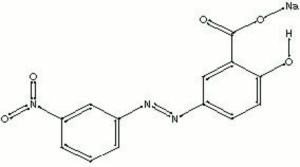
Alizarin yellow
Description
Alizarin yellow crystallizes as orange-brown needles from a dilute glacial Acetic acid solution. Developed in 1887 by R. Nietzki, it became the first azo Mordant dye. Alizarin yellow produces a dull yellow-brown, transparent pigment when precipitated on an inert base that has poorer color stability than alizarin. The sodium salt of alizarin yellow is used as an aqueous acid-base indicator. It changes from yellow at pH 10.2 to red at pH 12.0.
Synonyms and Related Terms
Mordant Yellow 1; CI 14030; alizarine yellow R; p-nitrophenylazosalicylate acid; 2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)azo]benzoic acid; amarilo de alizarina (Esp.); jaune d'alizarine (Fr.); giallo d'alizarina (It.); amarelo de alizarina (Port.)
Risks
Fisher Scientific: MSDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in water and ethanol. Slightly soluble in acetone and Cellosolve®. Insoluble in other organic solvents.
| Composition | C13H9N3O5 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 584-42-9 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 309.20 |
Resources and Citations
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- A.Scharff, 'Synthetic dyestuffs for textiles and their fastness to washing', ICOM-CC Preprints Lyon, Getty Conservation Institute, Los Angeles, 1999 Comment: p.654-660
- Colour Index International online at www.colour-index.org Comment: developer, date, CAS#=584-42-9, structure verified
- Sigma Dyes, Stains and Natural Pigments, Infrared Library, Nicolet, 1991-1995 Comment: CAS#=2243-76-7
- Website: www.straw.com/sig/dyehist
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000