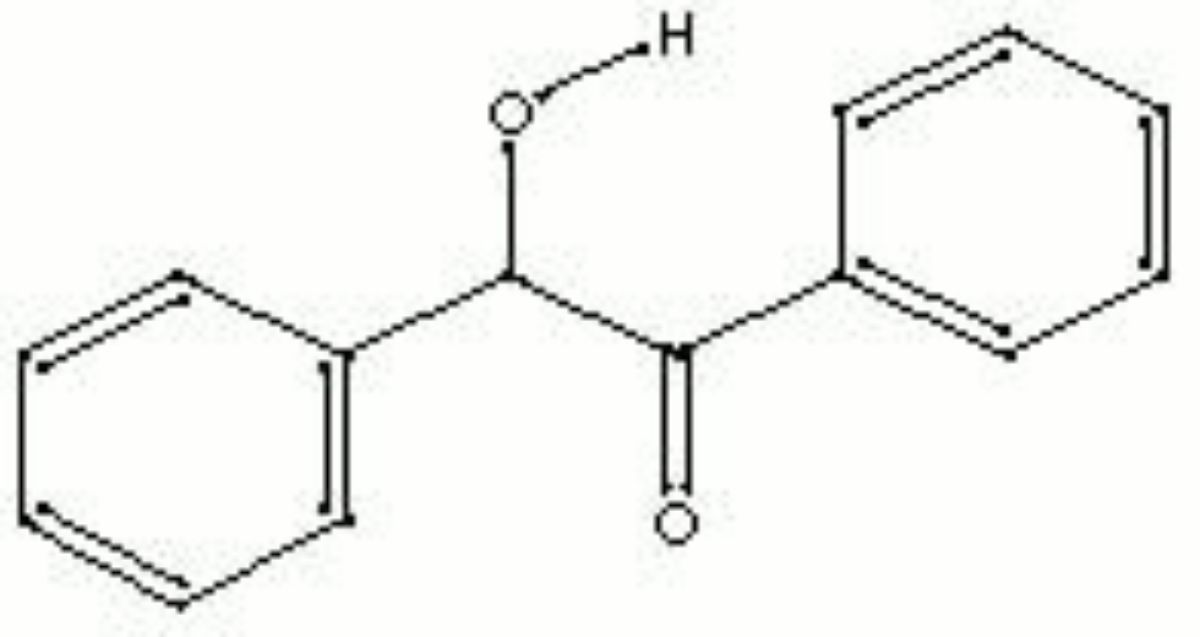
Benzoin
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Description
A white or yellowish crystalline powder derived from benzaldehyde. Benzoin is used in organic synthesis.
Note: Pure benzoin is not the same as benzoin resin.
Synonyms and Related Terms
bitter almond oil camphor; benzoylphenyl carbinol; 2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetophenone; phenylbenzoylcarbinol
Risks
- Combustible.
- Highly toxic.
- Fisher Scientific: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in acetone, hot ethanol. Slightly soluble in water, ether.
| Composition | C6H5CH2OCOC6H5 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 119-53-9 |
| Melting Point | 137 C |
| Density | 1.310 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 212.2 |
| Boiling Point | 344 C |
Resources and Citations
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 1124
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998