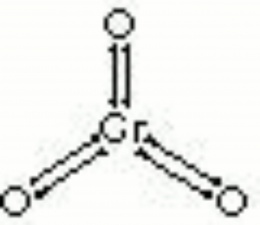
Chromic acid
Description
Dark red deliquescent crystals of Chromium trioxide. Chromic acid is made by mixing Potassium dichromate and an acid such as Hydrochloric acid or Sulfuric acid. It is an extremely strong oxidizing agent that will react violently with any organic compound. For many years, chromic acid was used in chemical laboratories cleaning baths to remove all traces of organic residues from glassware (see Beckmann mixture). Chromic acid is also used for chrome plating baths, engraving etching, tanning and as a colorant in glass and ceramics. This corrosive compound was also used to dye wood, bone, and ivory black.
Synonyms and Related Terms
chromium (IV) oxide; chromic trioxide; chromium trioxide; chromic anhydride;
Risks
- Powerful oxidizing agent, may explode on contact with reducing agents.
- Toxic by ingestion.
- Contact will corrode skin and membranes.
- LabChem: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in water, ethanol, mineral acids.
| Composition | CrO3 (in water-H2CrO4) |
|---|---|
| CAS | 1333-82-0 |
| Melting Point | 197 C |
| Density | 2.7 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 100.01 |
Resources and Citations
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p.192
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Susan E. Schur, Conservation Terminology: A review of Past & Current Nomenclature of Materials, Technology and Conservation, Spring (p.34-39); Summer (p.35-38); Fall (p.25-36), 1985
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 2293
- Jonathan Thornton, JAIC 43. p 274, Submitted information.
- Conservation termlist at www.hants.org.uk/museums