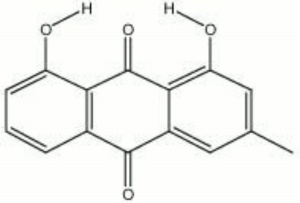
Chrysophanic acid
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Description
A natural yellow dyestuff found in the roots of rhubarb plants and also in a yellow colored lichen, Xanthoria parietina, in the form of parietin. Chrysophanic acid is extracted from the ground plant in an alkaline solution. The yellow colorant precipitates when the solution is neutralized with an acid.
Synonyms and Related Terms
Xanthoria parietina; 1,8-dihydroxy-3-methylanthraquinone; chrysophanol; 3-methylchrysazin; 1,8-dihydroxy-3-methyl-9,10-anthracenedione; rhenic acid; acido crisofanico (It.)
Risks
- Contact may cause irritation.
- Ingestion may cause nausea and vomiting.
- Fisher Scientific: MSDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Soluble in ethanol, benzene, chloroform, ether, acetone, acids, alkalis. Insoluble in water.
- Absorption max. = 226, 256, 278, 288, 436 nm.
| Composition | C15H10O4 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 481-74-3 |
| Melting Point | 196 C |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt.=254.24 |
Resources and Citations
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 2318
- F. Crace-Calvert, Dyeing and Calico Printing, Palmer & Howe, London, 1876 Comment: pp. 296 and 298
- Sigma Dyes, Stains and Natural Pigments, Infrared Library, Nicolet, 1991-1995 Comment: OMNIC: formula= C15H10O4, CAS= 481-74-3