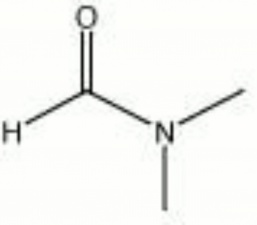
Dimethylformamide
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Description
A clear, toxic liquid that is considered a universal Solvent since it is miscible in both water and organic solvents. Dimethylformamide (DMF) dissolves most natural and synthetic resins, and, with heat and time, DMF will even soften Epoxy. It is often used in liquid chromatographic systems as a gradient intermediate between polar and nonpolar solvents. DMF is also used in some commercial paint stripping formulations.
Synonyms and Related Terms
DMF; DMFA; n,n-dimethyl formamide
Risks
- Carcinogenic.
- Overexposure may cause vomiting, liver damage and high blood pressure.
- Irritant to skin.
- Combustible; moderate fire risk. Flash point = 58C
- Toxic by inhalation, ingestion and skin absorption.
- Greenfield: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Miscible with water and most common organic solvents.
| Composition | HCON(CH3)2 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 68-12-2 |
| Melting Point | -61 C |
| Density | 0.9445 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 73.09 |
| Boiling Point | 153 C |
Comparisons
Resources and Citations
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 9232
- Hermann Kuhn, Conservation and Restoration of Works of Art and Antiquities, Butterworths, London, 1986