Elemi
Description
A soft, sticky natural resin derived from trees of the family Burseraceae. Because of the high oil content of the elemi resins, the term was used in the 17th and 18th centuries to describe many oleoresin mixtures. Currently the most common is Manila elemi, a malleable resin with a pungent odor obtained from the Pili trees, Canarium luzonicum and Canarium communis, of the Philippines. Other elemi resins come from Amyris elemifera (Egypt) and Elaphirium elemiferum (Mexico). Elemi has been used as a plasticizer in varnishes, but the components responsible for its initial malleability (mono- and sesquiterpenoids) evaporate and it eventually hardens to a brittle film. Elemi is used in lithographic inks, textile coatings, paper coatings, perfume bases, and waterproofing.
Synonyms and Related Terms
elemi (Deut., Esp., It., Pol.); elemi gum; Luzon; Manila elemi; Nauli elemi; gum elemi; canarium; elemi resin
Physical and Chemical Properties
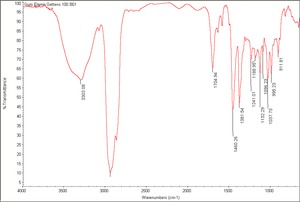
- Soluble in ethanol, ether, chloroform, benzene. Insoluble in water, turpentine and mineral spirits.
- Contains phellandrene, dipentene, elemol, elemicin, terpineol, carvone and terpinolene.
- Saponification number = 25-50.
- Acid number = 17.8-25.
- Melting Point = 177-121 C
Comparisons
Resources and Citations
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 291
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Kurt Wehlte, The Materials and Techniques of Painting, Van Nostrand Reinhold Co., New York, 1975
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "Burseraceae." Accessed 14 Apr. 2004 .
- "Violin Varnish Glossary" at www.violins.on.ca/luthier.vargloss.html - gives tree name as Cananarium commune
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Elemi
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, https://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000