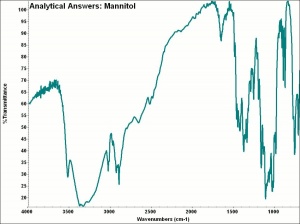
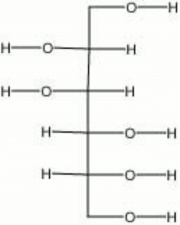
Mannitol
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Description
A sweet-tasting, crystalline powder. Mannitol occurs naturally in plants and seaweeds. Mannitol will liquefy any gum solution that has been gelled with borate because it reacts with borates to form mannitoborate. Examples of gums that gel with borate are Gum arabic, Locust bean gum, and gum guar. Mannitol has been used in conjunction with Sucrose for the impregnation of waterlogged wood (Morgos and Imazu, 1993).
Synonyms and Related Terms
manna sugar; mannite; cordycepic acid
Risks
- Combustible.
- ThermoFisher: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in water, pyridine, aniline and dilute alkalis. Slightly soluble in alcohols and amines. Insoluble in other organic solvents.
| Composition | C8H8(OH)6 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 69-65-8 |
| Melting Point | 166-168 C |
| Density | 1.52 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 182.17 |
| Boiling Point | 290-295 |
Resources and Citations
- A Morgos, S.Imazu "A Conservation Method for Waterlogged Wood using a Sucrose-Mannitol Mixture" ICOM Preprints, Washington DC, 1993, p.266-272.
- The Merck Index, Susan Budavari (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Whitehouse Station, NJ, 12th Edition, 1996 Comment: entry 5788
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993