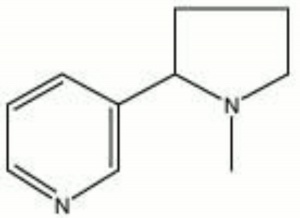
Nicotine
Description
A colorless, oily liquid alkaloid primarily obtained from the dried leaves of the tobacco plant (Nicotiana tabacum). Nicotine was named in 1550 for Jean Nicot after he sent tobacco seeds to Paris. It is a highly additive drug that is toxic in large doses. Commercially, purified nicotine is used as an Insecticide, parasiticide, and Fumigant. Nicotine turns brown when exposed to light or air.
Synonyms and Related Terms
1-methyl-2-(3-pyridyl)pyrrolidine; 3-(1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)pyridine; Nikotin (Deut.); nicotina (Esp., It., Port.); nicotine (Fr., Ned.); nikotyna (Pol.); nikotin (Sven.); Black Leaf 40; Ortho-N4 dust; Niagara P.A. dust; Nicocide; Nico-dust; Nico-fume; Nicotina; Destruxol orchid spray; Emo-n; Flux MAAG; Fumetobac; Mach-Nic;
Risks
- Toxic by inhalation, ingestion and skin absorption.
- Combustible. Flash point = 95 C
- Gives off toxic fumes.
- ThermoFisher: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Miscible with water. Soluble in alcohols, chloroform, ether, kerosene, oils.
Hygroscopic. Turns brown with exposure to air and light.
| Composition | C10H14N2 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 54-11-5 |
| Melting Point | -8.0 C |
| Density | 1.01 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 162.23 |
| Boiling Point | 123-125 C |
Resources and Citations
- The Merck Index, Susan Budavari (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Whitehouse Station, NJ, 12th Edition, 1996 Comment: entry 6365; b.p.=123-125C
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "nicotine" [Accessed March 26, 2002
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nicotine (Accessed Nov. 9, 2005) - b.p.=247C