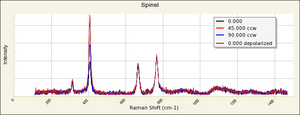
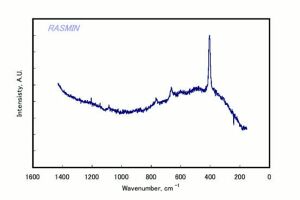
Spinel
Description
A hard, colored gemstone. Spinels are composed of magnesium aluminum oxide with color-producing traces of iron, zinc, chromium, or manganese. Bright red (Balas) and deep blue spinels were sometimes confused with rubies and sapphires. Spinels can also be violet (Almandine), pink, yellow (rubicelle), green, brown, or black. Spinels have been mined since at least 1000 BCE. Early deposits were found in the alluvial gravels of Sri Lanka, in limestones of Myanmar (Burma) and Thailand, and near Oxus in the Middle East. Currently, spinels are also mined in Russia, Italy, Sweden, Germany, Canada (Ontario), and the U.S. (New York, New Jersey, New Mexico, North Carolina, California). Spinels are also made synthetically as magnesia-alumina or magnesia-chromia. Industrially, the synthetic spinels are used in electronics and as refractory materials. Colorless synthetic spinels are sold as diamond substitutes in gemstone settings.
Synonyms and Related Terms
spinelle; Balas rubies (red); spinel rubies (red); ruby spinel; magnesia spinel; rubicelle (yellow); almandine (violet); pleonast (blue, dark green, black); hercynite (iron aluminum oxide-black); gahnite (zinc aluminum oxide-dark blue-green); galaxite (manganese aluminum oxide-black); Spinell (Deut., Sven.); espinela (Esp., Port.); spinelle (Fr.); spinel (Ned.)
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Cubic crystal system with crystals as octahedrals or flat twinned plates
- Fracture = conchoidal
- Streak = white
- Luster = vitreous to subadamantine
- Fluorescence = Natural spinel may fluoresce under LW, but not SW; synthetic spinel often shows colors in SW
- Pleochroism = none
- Birefringence = none
- Magnetism = weak to medium
- Inclusions = minute crystals alone or in fingerprint patterns; iron-oxide staining
| Composition | MgAl2O4 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 1302-67-6 |
| Mohs Hardness | 7.5 - 8.0 |
| Density | 3.5-4.1 g/ml |
| Refractive Index | 1.715-1.725 |
Comparisons
Properties of Common Gemstones
Natural and Simulated Diamonds
Resources and Citations
- Gem Identification Lab Manual, Gemological Institute of America, 2016.
- Mineralogy Database: Spinel
- Jack Odgen, Jewellery of the Ancient World, Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982
- R.F.Symmes, T.T.Harding, Paul Taylor, Rocks, Fossils and Gems, DK Publishing, Inc., New York City, 1997
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "spinel" [Accessed December 11, 2001].
- Website: http://www.geo.utexas.edu/courses/347k/redesign/gem_notes/Spinel/spinel_triple.htm (fluorescence information)
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Wikipedia: Spinel (Accessed Sept. 17, 2005 and Jan 2023)
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 751
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Walter C. McCrone, John Gustave Delly, The Particle Atlas, W. McCrone Associates, Chicago, IV, 1972
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998