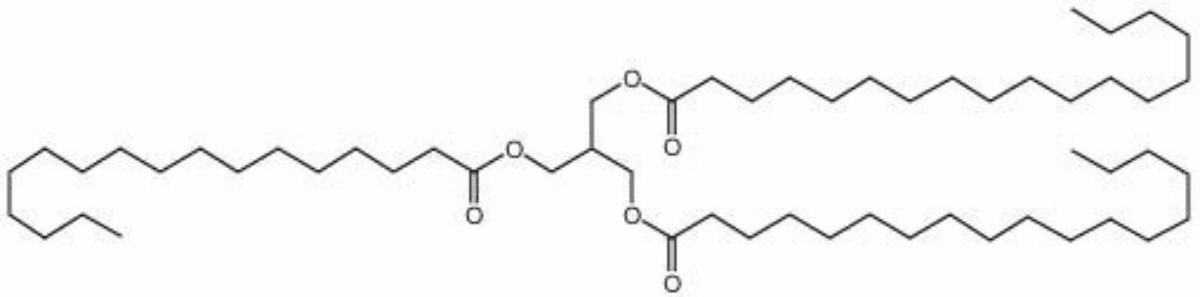
Tristearin
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Description
A colorless, odorless, white powder. Tritearin, or stearin, is found in most animal and vegetable fats especially hard ones like cocoa butter and tallow. It is the glyceride of stearic acid. Stearin is used in the manufacture of soaps, candles, adhesives, metal polishes, waterproofing paper, textile sizes, and leather stuffing.
Synonyms and Related Terms
octadecanoic acid 1,2,3-propanetriyl ester; triestearina (Esp.); stearina (It); stearin; glycerol tristearate; glyceryl tristearate
Risks
- Combustible.
- Contact may cause irritation.
- Fisher Scientific: MSDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in benzene, chloroform, carbon disulfide, hot ethanol. Insoluble in water.
| Composition | C3H5(C18H35O2)3 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 555-43-1 |
| Melting Point | 71.6 C |
| Density | 0.862 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 891.50 |
| Refractive Index | 1.4385 |
Resources and Citations
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 771
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 9885
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998