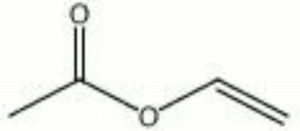
Vinyl acetate
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Description
A colorless liquid used in the production of several polymers, i.e., Polyvinyl acetate, Polyvinyl alcohol, Polyvinyl butyral, and Polyvinyl chloride acetate. The process for making vinyl acetate was first patented in 1958 by Celanese.
Synonyms and Related Terms
acetic acid ethenyl ester; acetic acid vinyl ester; vinyl acetate monomor (VAM); a-acetoxyethylene
Risks
- Flammable.
- Toxic by inhalation and ingestion.
- Contact causes irritation.
- ThermoFisher: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in most organic solvents. Insoluble in water.
| Composition | CH3COOCH:CH2 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 108-05-4 |
| Melting Point | -100.2 C |
| Density | 0.9345 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 86.09 |
| Refractive Index | 1.3941 |
| Boiling Point | 72.7 C |
Resources and Citations
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 10130
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vinyl_acetate (Accessed Jan. 6 2006)