Zircon
Description
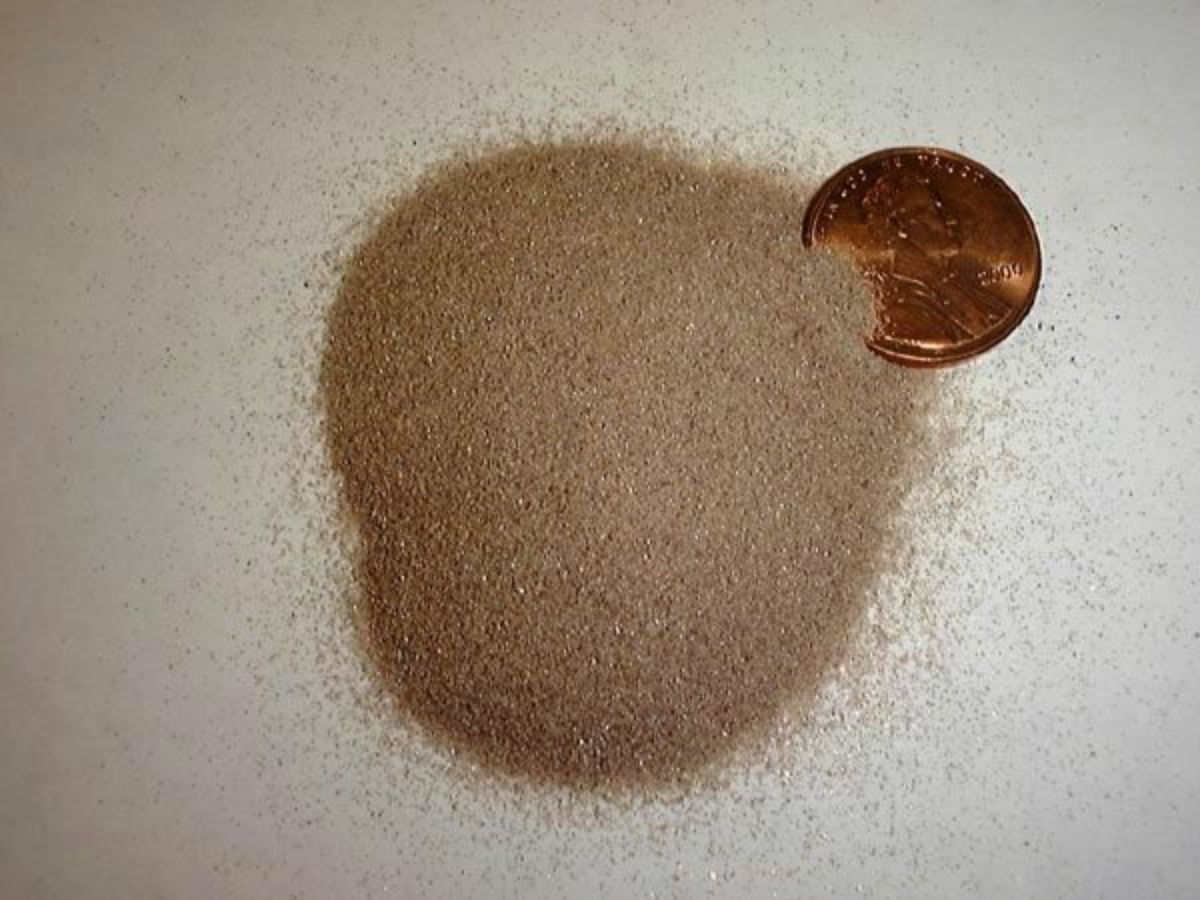
A natural mineral ore of zirconium silicate primarily used to produce zirconium. The zircon tetragonal prism crystals are found on beaches or in river placer deposits in association with silica containing minerals. The hard, refractory, but brittle crystals come in a wide range of colors: yellow, green, blue, red to brown. Clear zircon crystals, sold as Matura diamonds, make very brilliant gemstones because of their high refractive index. Clear yellow to red zircon, called hyacinth or jacinth, is also used as a gem. Ancient gems of hessonite garnets were also called jacinth and hyacinth which led to some being incorrectly labeled zircon (Ogden 1982). Zircons from Sri Lanka have been used for 2000 years. Large deposits are found in Australia. Other sources are Brazil, India, Pakistan, Thailand, New Zealand, Myanmar (formerly Burma), Western Africa, Norway (Seiland), Russia, Canada (Ontario) and the U.S. (Florida, Colorado, South Carolina, New Jersey).
Synonyms and Related Terms
zirconium silicate; zirkelite; zirconite; zircon sand; Matura diamonds; jacinth; hyacinth; jargoon; jargon; Zircopax [Titanium Alloy Mfg.]; Superpax; Ultrox [M&T Chemical]; cubic zirconia; Zirkon (Deut.); zircón (Esp.); circón (Esp.); zircon (Fr.); zirkoon (Ned.); cyrkon (Pol.); zircão (Port.)
Risks
- Contact and inhalation of zirconium compounds may cause nodules under the skin and in the lungs.
- Fisher Scientific: MSDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Insoluble in acids
- Tetragonal system with tabular to prismatic crystals
- Fracture = conchoidal to uneven
- Luster = adamantine to vitreous
- Streak = colorless
- Pleochroism = moderate purplish red to brown dichroism
- Fluorescence = some show dull yellow color; some may phosphoresce. Not diagnostic.
- Birefringence = 0 to 0.059
Heating brown zircon crystals produces strong colors (blue, green, red, etc.) that fade slowly with time or with UV exposure.
| Composition | ZrSiO4 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 14940-68-2 |
| Mohs Hardness | 6.0 - 7.5 |
| Melting Point | 2550 C |
| Density | 4.0-4.7 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 183.31 |
| Refractive Index | 1.94; 1.98 |
| Dispersion | 0.038 (moderate fire sometimes masked by body color) |
Comparisons
Properties of Common Gemstones
Natural and Simulated Diamonds
Resources and Citations
- Gem Identification Lab Manual, Gemological Institute of America, 2016.
- Jack Odgen, Jewellery of the Ancient World, Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982
- R.F.Symmes, T.T.Harding, Paul Taylor, Rocks, Fossils and Gems, DK Publishing, Inc., New York City, 1997
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "zircon" [Accessed December 11, 2001]. (color photo and tech Info)
- Website: http://www.geo.utexas.edu/courses/347k/redesign/gem_notes/Zircon/zircon_triple.htm (fluorescence information)
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Wikipedia: Zircon (Accessed Sept. 20, 2005 and Jan 2023)
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 890
- The Merck Index, Susan Budavari (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Whitehouse Station, NJ, 12th Edition, 1996 Comment: entry 9986
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979