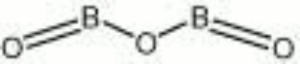Difference between revisions of "Boric oxide"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
LINK: [http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/ipcsneng/neng0836.html International Chemical Safety Card] | LINK: [http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/ipcsneng/neng0836.html International Chemical Safety Card] | ||
| − | == | + | == Sources Checked for Data in Record == |
* Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | ||
Revision as of 13:12, 29 April 2016
Description
A colorless crystalline compound used in metallurgy and in the manufacture of heat-resistant (borosilicate) glassware. Boric oxide is obtained from Boric acid, Borax, Sodium borate, or Colemanite. It is used in combination with silica as a flux for glazes.
Synonyms and Related Terms
boron oxide; boric anhydride; boron trioxide; boron sesquioxide
Other Properties
Soluble in ethanol, hot water.
| Composition | B2O3 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 1303-86-2 |
| Melting Point | 450 |
| Density | 2.46 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 69.6 |
| Boiling Point | 1500 |
Hazards and Safety
Noncombustible.
LINK: International Chemical Safety Card
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Henry Hodges, Artifacts: An Introduction to Early Materials and Technology, Ronald P. Frye, Kingston, Canada, 1988
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997