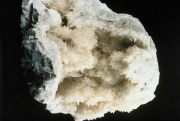
Colemanite
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Description
A mineral composed of hydrated Calcium borate. Colemanite occurs in massive deposits and monoclinic crystals. Named after William T. Coleman, the mineral was originally found in 1884 in Death Valley, California. It is currently mined in Turkey. Colemanite can be colorless, milky or gray and transparent to translucent. It is a principal source of Borax and Boric acid. Colemanite is used in the manufacture of Glass, glass fibers, and ceramic glazes.
Synonyms and Related Terms
hydrated calcium borate; Gerstley borate; colémanite (Fr.); colémanita (Esp.); Colemanit (Deut.)
Risks
- Contact and ingestion will burn skin and tissues
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Monoclinic system with prismatic crystals or massive or granular.
- Perfect cleavage in one direction; good in a second direction.
- Luster = vitreous to adamantine.
- Fracture = subconchoidal.
- Streak = white.
| Composition | Ca2B6O11-5H2O |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 4.0 - 4.5 |
| Density | 2.26-2.48 g/ml |
| Refractive Index | 1.445;1.469;1.472 |
Resources and Citations
- Mineralogy Database: Colemanite
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- Robert Fournier, Illustrated Dictionary of Practical Pottery, Chilton Book Company, Radnor, PA, 1992
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "colemanite" [Accessed December 4, 2001 (B/W photo)
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Colemanite (Accessed Sept 2 2005, harddddddness = 4.5, spec. gravity=2.42)
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998