Difference between revisions of "Copper chloride"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
cupric chloride; copper (II) chloride | cupric chloride; copper (II) chloride | ||
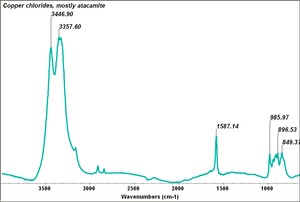
| − | [[[SliderGallery rightalign| | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Copper chlorides, mostly atacamite.TIF~FTIR (MFA)|copper chloride.jpg~Chemical structure]]] |
== Other Properties == | == Other Properties == | ||
Revision as of 08:54, 15 October 2019
Description
Anhydrous copper chloride has dark yellow crystals that absorb water to form green deliquescent crystals. Copper chloride is used as a Disinfectant, Fungicide, and Wood preservative. It is also used as a fixer in photography, a Mordant in dyeing textiles and a component in indelible inks. In metallurgy, copper chloride is used refine Gold and Silver, to recover Mercury from ore, and to electroplate Copper on Aluminum. Copper chloride is also used as a Glass and ceramics pigment.
Synonyms and Related Terms
cupric chloride; copper (II) chloride
Other Properties
Soluble in alcohols, water and acetone. Aqueous solution is acidic.
| Composition | CuCl2 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 7447-39-4 |
| Density | 2.54 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 134.45 |
| Refractive Index | 1.644, 1.684, 1.742 |
Hazards and Safety
Toxic by ingestion and inhalation. Skin contact causes irritation.
Mallinckrodt Baker: MSDS
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 2699
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: ref. index=1.644, 1.684, 1.742