Difference between revisions of "Softwood"
JMcGlinchey (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | One of two common classifications for trees, [ | + | One of two common classifications for trees, [[hardwood|hardwood]] (angiosperm) and softwood (gymnosperm). Softwoods are coniferous trees. With the exception of the larch and cypress trees, softwoods do not shed their needle-like leaves. Examples of softwood trees are: [[pine|pine]], [[fir|fir]], [[hemlock|hemlock]], [[spruce|spruce]], [[tamarack|tamarack]], [[cedar wood|Cedar]], and [[redwood|redwood]]. Softwood trees are found in temperate and mountainous regions. Most of softwoods are used for general construction, fences, and paper pulp. Softwood trees tend to have less acetic acid (1-2%) than hardwoods (3-5%) (Hatchfield 2002). |
[[File:99_Chem. softwood_conif_pol adj.jpg|thumb|Chemical softwood (coniferous)]] | [[File:99_Chem. softwood_conif_pol adj.jpg|thumb|Chemical softwood (coniferous)]] | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
nanboku (Jap.); bois tendre (Fr.); legno di conifera (It.); evergreen; coniferous | nanboku (Jap.); bois tendre (Fr.); legno di conifera (It.); evergreen; coniferous | ||
| − | == | + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == |
Contain tracheids rather than pores. May contain resin channels. | Contain tracheids rather than pores. May contain resin channels. | ||
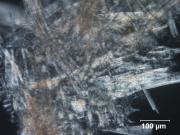
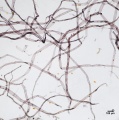
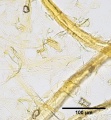
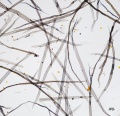
| − | Paper fiber type: Softwood. Using transmitted light microscopy, softwood fibers are identified by the presence of intertrachied "bordered" pits and species specific features such as ray parenchyma pits, size, width, etc. Appearance with [[Graff "C" stain]]: [[sulfite process|sulfite]]= warm pink to grey, appearance gets lighter with progressive bleaching, [[kraft process|kraft]]=grey blue to purple, appearance gets lighter with progressive bleaching. Average dimensions of fibers: species dependent. Common pulping method: [[kraft process|kraft]] and [[sulfite process|sulfite]] | + | Paper fiber type: Softwood. Using transmitted light microscopy, softwood fibers are identified by the presence of intertrachied "bordered" pits and species specific features such as ray parenchyma pits, size, width, etc. Appearance with [[Graff "C" stain]]: [[sulfite process|sulfite]]= warm pink to grey, appearance gets lighter with progressive bleaching, [[kraft process|kraft]]=grey blue to purple, appearance gets lighter with progressive bleaching. Average dimensions of fibers: species dependent (average= 3-3.6mm). Common pulping method: [[kraft process|kraft]] and [[sulfite process|sulfite]]. The long fibers of softwood pulp impart strength to paper and are often used in conjunction with [[hardwood]] and [[rag]] pulps. Softwood can be pulped [[mechanical wood pulp|mechanically]] or [[chemical wood pulp|chemically]]. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Additional Images == | == Additional Images == | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
| − | File:SWBS puget 10x label.jpg|Softwood bleached sulfite paper pulp | + | File:SWBS puget 10x label.jpg|Softwood bleached sulfite paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain |
| − | File:SUBK 10x2 label.jpg|Softwood unbleached kraft paper pulp | + | File:SUBK 10x2 label.jpg|Softwood unbleached kraft paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain |
| − | File:SWGW 40x label.jpg|Softwood groundwood paper pulp | + | File:SWGW 40x label.jpg|Softwood groundwood paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain |
| − | File:SBA 40x pinoidpitslabel.jpg|Softwood bleached alpha paper pulp | + | File:SBA 40x pinoidpitslabel.jpg|Softwood bleached alpha paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain |
| − | File:W red cedar 40x.jpg| | + | File:W red cedar 40x.jpg|Example of pitting in softwood fibers stained with Graff "C" stain |
| + | Red pine 10x.jpg|Red pine paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | ||
| + | SWUBK sugar pine 40x.jpg|Sugar paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | ||
| + | Larch 10x.jpg|Larch paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | ||
| + | Douglas fir 40x spirals.jpg|Douglas fir paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | ||
| + | Spruce 40x 4.jpg|Spruce paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | + | * Alden Identification Services, Microscopic Wood Identification: [https://wood-identification.com/wood-types/ Link] | |
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 875 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 875 | ||
| Line 39: | Line 40: | ||
* Pam Hatchfield, ''Pollutants in the Museum Environment'', Archetype Press, London, 2002 | * Pam Hatchfield, ''Pollutants in the Museum Environment'', Archetype Press, London, 2002 | ||
| − | * | + | * AMOL reCollections Glossary -http://amol.org.au/recollections/7/c/ |
| − | * | + | * Museum of Japanese Traditional Art Crafts at http://www.nihon-kogeikai.com/ (Jap. term) |
* Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | * Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | ||
Latest revision as of 12:31, 12 October 2020
Description
One of two common classifications for trees, Hardwood (angiosperm) and softwood (gymnosperm). Softwoods are coniferous trees. With the exception of the larch and cypress trees, softwoods do not shed their needle-like leaves. Examples of softwood trees are: Pine, Fir, Hemlock, Spruce, Tamarack, Cedar, and Redwood. Softwood trees are found in temperate and mountainous regions. Most of softwoods are used for general construction, fences, and paper pulp. Softwood trees tend to have less acetic acid (1-2%) than hardwoods (3-5%) (Hatchfield 2002).
Synonyms and Related Terms
nanboku (Jap.); bois tendre (Fr.); legno di conifera (It.); evergreen; coniferous
Physical and Chemical Properties
Contain tracheids rather than pores. May contain resin channels.
Paper fiber type: Softwood. Using transmitted light microscopy, softwood fibers are identified by the presence of intertrachied "bordered" pits and species specific features such as ray parenchyma pits, size, width, etc. Appearance with Graff "C" stain: sulfite= warm pink to grey, appearance gets lighter with progressive bleaching, kraft=grey blue to purple, appearance gets lighter with progressive bleaching. Average dimensions of fibers: species dependent (average= 3-3.6mm). Common pulping method: kraft and sulfite. The long fibers of softwood pulp impart strength to paper and are often used in conjunction with Hardwood and Rag pulps. Softwood can be pulped mechanically or chemically.
Additional Images
Resources and Citations
- Alden Identification Services, Microscopic Wood Identification: Link
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 875
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Pam Hatchfield, Pollutants in the Museum Environment, Archetype Press, London, 2002
- AMOL reCollections Glossary -http://amol.org.au/recollections/7/c/
- Museum of Japanese Traditional Art Crafts at http://www.nihon-kogeikai.com/ (Jap. term)
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- Marja-Sisko Ilvessalo-Pfäffli. Fiber Atlas: Identification of Papermaking Fibers (Springer Series in Wood Science). Springer, 1995.
- Walter Rantanen. "Fiber ID Course." Integrated Paper Services. June 2013. Lecture.