Difference between revisions of "Wool"
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
[[File:sheepkes.jpg|thumb|Sheep]] | [[File:sheepkes.jpg|thumb|Sheep]] | ||
| + | [[File:Wool 200x BF.POL.jpg|thumb|Wool fibers]] | ||
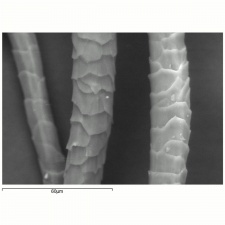
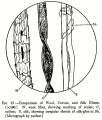
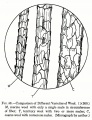
Textile fibers obtained from the fleece of sheep. The term wool is also used for a small amount of hair that is obtained from [[camel%20hair|camels]], [[alpaca|alpacas]], Angora rabbits ([[angora|angora]]), Angora goats ([[mohair|mohair]]), Kashmir goats ([[cashmere|cashmere]]), [[llama|llamas]], and [[vicu%C3%B1a|vicuñas]]. Wool, or hair, fibers are composed of [[keratin|keratin]]. Wool has been used by man since Neolithic times. The Phoenicians exported wool as early as the 7th century BCE. Sheep were brought to England in the 6th c. BCE and Britain has been the established leader in world wool trade since at least the 14th century CE. Wool fibers have a hollow core, or medulla, surrounded by a shaft called the cortex. The cortex is covered with a layer of scale-like cells, called epithelial scales. The size and shape of the scales are characteristic of the source of the fiber. The scales are usually coated with a thin outer sheath called the epicuticle. Wool fibers can range in color from white to brown to black. The fleece is obtained by shearing the sheep. | Textile fibers obtained from the fleece of sheep. The term wool is also used for a small amount of hair that is obtained from [[camel%20hair|camels]], [[alpaca|alpacas]], Angora rabbits ([[angora|angora]]), Angora goats ([[mohair|mohair]]), Kashmir goats ([[cashmere|cashmere]]), [[llama|llamas]], and [[vicu%C3%B1a|vicuñas]]. Wool, or hair, fibers are composed of [[keratin|keratin]]. Wool has been used by man since Neolithic times. The Phoenicians exported wool as early as the 7th century BCE. Sheep were brought to England in the 6th c. BCE and Britain has been the established leader in world wool trade since at least the 14th century CE. Wool fibers have a hollow core, or medulla, surrounded by a shaft called the cortex. The cortex is covered with a layer of scale-like cells, called epithelial scales. The size and shape of the scales are characteristic of the source of the fiber. The scales are usually coated with a thin outer sheath called the epicuticle. Wool fibers can range in color from white to brown to black. The fleece is obtained by shearing the sheep. | ||
| − | + | ||
* For wool fiber identification, see http://cameo.mfa.org/wiki/Category:FRIL:_Wool | * For wool fiber identification, see http://cameo.mfa.org/wiki/Category:FRIL:_Wool | ||
Revision as of 13:55, 13 October 2020
Description
Textile fibers obtained from the fleece of sheep. The term wool is also used for a small amount of hair that is obtained from camels, alpacas, Angora rabbits (Angora), Angora goats (Mohair), Kashmir goats (Cashmere), llamas, and vicuñas. Wool, or hair, fibers are composed of Keratin. Wool has been used by man since Neolithic times. The Phoenicians exported wool as early as the 7th century BCE. Sheep were brought to England in the 6th c. BCE and Britain has been the established leader in world wool trade since at least the 14th century CE. Wool fibers have a hollow core, or medulla, surrounded by a shaft called the cortex. The cortex is covered with a layer of scale-like cells, called epithelial scales. The size and shape of the scales are characteristic of the source of the fiber. The scales are usually coated with a thin outer sheath called the epicuticle. Wool fibers can range in color from white to brown to black. The fleece is obtained by shearing the sheep.
- For wool fiber identification, see http://cameo.mfa.org/wiki/Category:FRIL:_Wool
Synonyms and Related Terms
tweed; flannel; velour; felt; laine (Fr.); Wolle (Deut.); lana (Esp.); lana (It.); wol (Ned.); lã (Port.); ull (Sven.)
Risks
Damaged by alkalis and most bleach solutions. Decomposes in boiling water. Susceptible to moth larvae and other protein-feeding insects.
Physical and Chemical Properties
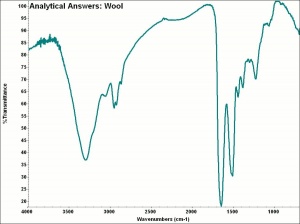
Fiber length = 38-125 mm (fine), 65-150 mm (medium),125-375 mm (long). Fiber width = 17 micrometers( fine), 24-34 micrometers (medium); 40 micrometers (long). Elongation = 25-35% (dry), 25-50% (wet) Moisture regain = 16-18% Wool chars producing the smell of burning hair. It will not continue to burn when the flame is removed.
| Melting Point | 130 (dec) |
|---|---|
| Density | 1.32-1.34 |
Comparisons
Additional Images
Resources and Citations
- G.Cook, Handbook of Textile Fibres:I. Natural Fibres, 5th edition, Merrow Publishing Co., Durham, England, 1984.
- Walter C. McCrone, John Gustave Delly, The Particle Atlas, W. McCrone Associates, Chicago, IV, 1972
- Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Dictionary of Fiber & Textile Technology (older version called Man-made Fiber and Textile Dictionary, 1965), Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Charlotte NC, 1990
- Rosalie Rosso King, Textile Identification, Conservation, and Preservation, Noyes Publications, Park Ridge, NJ, 1985
- A.Lucas, J.R.Harris, Ancient Egyptian Materials and Industries, Edward Arnold Publishers Ltd., London, 4th edition, 1962
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "wool" [Accessed November 7, 2001].
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wool (Accessed Nov. 29, 2005)
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- Website address 1 Comment: www.fabrics.net
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- Book and Paper Group, Paper Conservation Catalog, AIC, 1984, 1989
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000