Difference between revisions of "Xylose"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A pentose sugar with a sweet taste that is used as a sugar substitute. Xylose is a dextrorotatory white powder composed of colorless needle or prism crystals. It is derived from the hydrolysis of wood ([ | + | A pentose sugar with a sweet taste that is used as a sugar substitute. Xylose is a dextrorotatory white powder composed of colorless needle or prism crystals. It is derived from the hydrolysis of wood ([[maple|maple]] and [[cherry%20wood|cherry]]), [[straw|straw]], corn cobs, peanut shells, cottonseed hulls and wood pulp waste. Xylose is used in dyeing, tanning leather, and as a diabetic food. |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
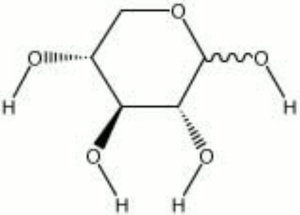
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|xylose.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|xylose.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | ||
| − | == | + | == Risks == |
| + | |||
| + | * Combustible. | ||
| + | * ThermoFisher: [https://www.fishersci.com/store/msds?partNumber=AC225990050&productDescription=L-%28-%29-XYLOSE%2C+P.A.+5GR&vendorId=VN00032119&countryCode=US&language=en SDS] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== | ||
Soluble in water, pyridine, ethanol. | Soluble in water, pyridine, ethanol. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 27: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | 144-145 | + | | 144-145 C |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 1.525 | + | | 1.525 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ||
| Line 31: | Line 36: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 781 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 781 | ||
| Line 43: | Line 42: | ||
* G.G. Hawley, ''The Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Reinhold Publishing, New York, 6th ed., 1961 | * G.G. Hawley, ''The Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Reinhold Publishing, New York, 6th ed., 1961 | ||
| − | * Wikipedia | + | * Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Xylose (accessed Mar. 10, 2006) |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:37, 22 June 2022
Description
A pentose sugar with a sweet taste that is used as a sugar substitute. Xylose is a dextrorotatory white powder composed of colorless needle or prism crystals. It is derived from the hydrolysis of wood (Maple and cherry), Straw, corn cobs, peanut shells, cottonseed hulls and wood pulp waste. Xylose is used in dyeing, tanning leather, and as a diabetic food.
Synonyms and Related Terms
wood sugar; Xylomed; Xylopfan
Risks
- Combustible.
- ThermoFisher: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in water, pyridine, ethanol.
| Composition | C5H10O5 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 58-86-6 |
| Melting Point | 144-145 C |
| Density | 1.525 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 150.14 |
Resources and Citations
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 781
- G.G. Hawley, The Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Reinhold Publishing, New York, 6th ed., 1961
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Xylose (accessed Mar. 10, 2006)