Difference between revisions of "Marble"
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:mMarble dog.jpg|thumb|Marble sculpture<br>MFA# 1973.601]] | [[File:mMarble dog.jpg|thumb|Marble sculpture<br>MFA# 1973.601]] | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | |||
A hard, dense, crystalline stone primarily composed of [[calcium%20carbonate|calcium carbonate]]. Marble is [[limestone|limestone]] or [[dolomite|dolomite]] that has been metamorphosed with heat and pressure. Pure calcite marble is white, but impurities produce a wide variety of coloring and patterns. Marble has fine grains and polishes to a smooth, high gloss. It is used for statuary and buildings. Marble has been quarried from sites around the world since at least the seventh century BCE. Historical quarry locations and marble types include: | A hard, dense, crystalline stone primarily composed of [[calcium%20carbonate|calcium carbonate]]. Marble is [[limestone|limestone]] or [[dolomite|dolomite]] that has been metamorphosed with heat and pressure. Pure calcite marble is white, but impurities produce a wide variety of coloring and patterns. Marble has fine grains and polishes to a smooth, high gloss. It is used for statuary and buildings. Marble has been quarried from sites around the world since at least the seventh century BCE. Historical quarry locations and marble types include: | ||
[[File:2002.630-SC53335.jpg|thumb|Marble relief<br>MFA# 2002.630]] | [[File:2002.630-SC53335.jpg|thumb|Marble relief<br>MFA# 2002.630]] | ||
| Line 21: | Line 20: | ||
==Physical and Chemical Properties== | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | ! scope="row"| Mineral | ||
| + | | Calcite or dolomite | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row"| Color | ||
| + | | typically white but impurities cause variations and patterns | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row"| Texture | ||
| + | | medium grains, soft and porous, easily stained and scratched | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row"| Chemical compatibility | ||
| + | | corroded by acids and alcohols | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Mohs Hardness | ! scope="row"| Mohs Hardness | ||
| Line 29: | Line 39: | ||
|} | |} | ||
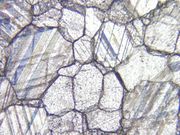
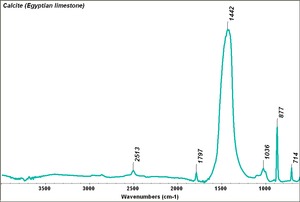
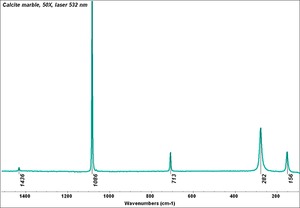
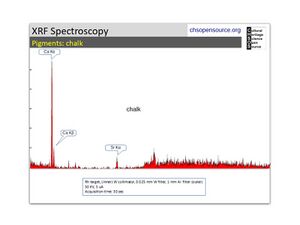
| − | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Calcite (Egyptian limestone).TIF~FTIR (MFA)||Calcite marble, 50X, laser 532 nm copy.tif~Raman (MFA)||mcalcite xrd.jpg~XRD]]] | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Calcite (Egyptian limestone).TIF~FTIR (MFA)||Calcite marble, 50X, laser 532 nm copy.tif~Raman (MFA)||mcalcite xrd.jpg~XRD|CHSOS XRF of Chalk.jpg~XRF (CHSOS)]]] |
== Resources and Citations == | == Resources and Citations == | ||
| − | |||
* Ralph Mayer, ''A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques'', Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing) | * Ralph Mayer, ''A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques'', Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing) | ||
| − | |||
* Michael McCann, ''Artist Beware'', Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979 | * Michael McCann, ''Artist Beware'', Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979 | ||
| − | |||
* ''Dictionary of Building Preservation'', Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996 | * ''Dictionary of Building Preservation'', Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996 | ||
| − | |||
* Thomas C. Jester (ed.), ''Twentieth-Century Building Materials'', McGraw-Hill Companies, Washington DC, 1995 | * Thomas C. Jester (ed.), ''Twentieth-Century Building Materials'', McGraw-Hill Companies, Washington DC, 1995 | ||
| − | |||
* Janet Burnett Grossman, ''Looking at Greek and Roman Sculpture in Stone'', J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2003 | * Janet Burnett Grossman, ''Looking at Greek and Roman Sculpture in Stone'', J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2003 | ||
| − | + | * Wikipedia: [|CHSOS XRF of Chalk.jpg~XRF (CHSOS) Marble] (Accessed Nov. 9, 2005 and April 2024) | |
| − | * Wikipedia: | ||
| − | |||
* Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | * Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | ||
| − | |||
* ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | * ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | ||
| − | |||
* ''CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics'', Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: density=2.6-2.84 (160-177 pounds per cubic foot) | * ''CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics'', Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: density=2.6-2.84 (160-177 pounds per cubic foot) | ||
Latest revision as of 12:50, 10 April 2024
Description
A hard, dense, crystalline stone primarily composed of Calcium carbonate. Marble is Limestone or Dolomite that has been metamorphosed with heat and pressure. Pure calcite marble is white, but impurities produce a wide variety of coloring and patterns. Marble has fine grains and polishes to a smooth, high gloss. It is used for statuary and buildings. Marble has been quarried from sites around the world since at least the seventh century BCE. Historical quarry locations and marble types include:
- Greece: Paros (Parian marble), Penteli (Pentelic marble), rosso antico, Eleusinian marble
- Turkey: Proconnesus
- Italy: Carrara, bardiglio, Cipollino marble (cipolin), parmazo marble
- Spain: Macael
- Belgium: rance, Belgian black, St. Anne marble
- France: Languedoc marble, griotte, Sarrancolin marble
- U.S.: Vermont white statuary, Georgia white, Colorado Yule statuary, Alabama cream, Tennessee pink, Rockingham royal black.
Note: Commercially, the term 'marble' is used for any non-granite stone that can take a polish, such as Travertine, Onyx, Serpentine, and Limestone.
Synonyms and Related Terms
calcium carbonate; marmer (Ned.); Marmor (Deut., Sven.); marbre (Fr.); marmo (It.); mármol (Esp.); marmur (Pol.); mármore (Port.);
Physical and Chemical Properties
| Mineral | Calcite or dolomite |
|---|---|
| Color | typically white but impurities cause variations and patterns |
| Texture | medium grains, soft and porous, easily stained and scratched |
| Chemical compatibility | corroded by acids and alcohols |
| Mohs Hardness | 3.0 |
| Density | 2.6-2.84 g/ml |
Resources and Citations
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- Dictionary of Building Preservation, Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996
- Thomas C. Jester (ed.), Twentieth-Century Building Materials, McGraw-Hill Companies, Washington DC, 1995
- Janet Burnett Grossman, Looking at Greek and Roman Sculpture in Stone, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2003
- Wikipedia: [|CHSOS XRF of Chalk.jpg~XRF (CHSOS) Marble] (Accessed Nov. 9, 2005 and April 2024)
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: density=2.6-2.84 (160-177 pounds per cubic foot)