Difference between revisions of "Dithizone"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
Blue-black crystalline powder used as a colorimetric reagent for the detction of [[zinc]] in metal objects, corrosion products, and [[pigment|pigments]] (Odegaard et al 2000). Zinc reacts with dithizone to produce a pink-red residue. Dithizone also reacts with [[silver]] (violet), [[copper]] (dark yellow), [[lead]] (dark red), and [[mercury]] (orange). | Blue-black crystalline powder used as a colorimetric reagent for the detction of [[zinc]] in metal objects, corrosion products, and [[pigment|pigments]] (Odegaard et al 2000). Zinc reacts with dithizone to produce a pink-red residue. Dithizone also reacts with [[silver]] (violet), [[copper]] (dark yellow), [[lead]] (dark red), and [[mercury]] (orange). | ||
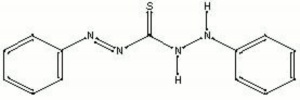
| − | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|dithizone.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
diphenylthiocarbazone; phenyldiazenecarbothioic acid 2-phenylhydrazide | diphenylthiocarbazone; phenyldiazenecarbothioic acid 2-phenylhydrazide | ||
| − | [ | + | == Risks == |
| + | |||
| + | * Contact may cause irritation. | ||
| + | * Fisher Scientific: [https://fscimage.fishersci.com/msds/96058.htm MSDS] | ||
| − | == | + | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== |
Insoluble in water. Soluble in carbon tetrachloride, chloroform Slightly soluble in alcohols. | Insoluble in water. Soluble in carbon tetrachloride, chloroform Slightly soluble in alcohols. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 25: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | 168 (dec) | + | | 168 C (dec) |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ||
| Line 28: | Line 31: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry #3395 | * ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry #3395 | ||
| − | * N.Odegaard, S.Carroll, W.Zimmt, ''Material Characterization Tests for Objects of Art and Archaeology'', Archetype Publications, London, 2000 | + | * N.Odegaard, S.Carroll, W.Zimmt, ''Material Characterization Tests for Objects of Art and Archaeology'', Archetype Publications, London, 2000, p.96. |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:21, 22 July 2022
Description
Blue-black crystalline powder used as a colorimetric reagent for the detction of Zinc in metal objects, corrosion products, and pigments (Odegaard et al 2000). Zinc reacts with dithizone to produce a pink-red residue. Dithizone also reacts with Silver (violet), Copper (dark yellow), Lead (dark red), and Mercury (orange).
Synonyms and Related Terms
diphenylthiocarbazone; phenyldiazenecarbothioic acid 2-phenylhydrazide
Risks
- Contact may cause irritation.
- Fisher Scientific: MSDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Insoluble in water. Soluble in carbon tetrachloride, chloroform Slightly soluble in alcohols.
| Composition | C13H12N4S |
|---|---|
| CAS | 60-10-6 |
| Melting Point | 168 C (dec) |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 256.32 |
Resources and Citations
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry #3395
- N.Odegaard, S.Carroll, W.Zimmt, Material Characterization Tests for Objects of Art and Archaeology, Archetype Publications, London, 2000, p.96.