Difference between revisions of "Platinum paper"
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File:1981.146-SC7826.jpg|thumb| | + | [[File:1981.146-SC7826.jpg|thumb|Yosemite Falls<br>MFA# 1981.146]] |
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | + | [[File:Baby_Plat.print_overall.jpg|thumb|Platinum print]] | |
A nonsilver photographic printing paper that used sodium or potassium tetrachloroplatinite as the light sensitive compound. Platinum was first used for photography in 1856 as an intensifier for silver prints. In 1873, William Willis patented the process for platinum printing in which paper is coated with a mixture of [[oxalic acid]] and [[potassium chloroplatinate]]. The [[iron]] is reduced with exposure to light then oxidized with a [[potassium oxalate]] developing solution with the concurrent reduction of fine-grain platinum. The prints are then fixed with a clearing solution containing [[ammonium hydroxide]] [[ammonium chloride]], [[oxalic acid]], [[sodium chloride]], and [[sodium hyposulfite]]. Platinum prints have a clear gray tonality, fine black details and a matte surface. They were discontinued by World War I due to the extremely high price of the metal. | A nonsilver photographic printing paper that used sodium or potassium tetrachloroplatinite as the light sensitive compound. Platinum was first used for photography in 1856 as an intensifier for silver prints. In 1873, William Willis patented the process for platinum printing in which paper is coated with a mixture of [[oxalic acid]] and [[potassium chloroplatinate]]. The [[iron]] is reduced with exposure to light then oxidized with a [[potassium oxalate]] developing solution with the concurrent reduction of fine-grain platinum. The prints are then fixed with a clearing solution containing [[ammonium hydroxide]] [[ammonium chloride]], [[oxalic acid]], [[sodium chloride]], and [[sodium hyposulfite]]. Platinum prints have a clear gray tonality, fine black details and a matte surface. They were discontinued by World War I due to the extremely high price of the metal. | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Baby2.jpg|thumb|Detail of platinum print of baby]] |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
platinotype; platinum print; potassium chloroplatinite paper | platinotype; platinum print; potassium chloroplatinite paper | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Additional Images == | == Additional Images == | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
| − | File: | + | File: platinum sample6 site2.jpg|SEM of platinum print sample 6 |
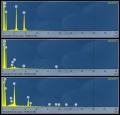
| − | + | File:platinum sample6 site2 Spectra 1-3.jpg|Spectra for sample 6 sites | |
| − | File:platinum sample6 site2 Spectra 1-3.jpg|Spectra | + | File:Woman.Plat.print sample 7 200x Refl.jpg|Platinum print sample 7 at 200x in reflected light |
| − | File: | + | File:Woman.Plat.print sample 7 200x UV.jpg|Platinum print sample 7, at 200x in UV light |
| − | File: | + | </gallery> |
| − | File: | + | <gallery> |
| − | File: | + | File:Woman_Plat.print_overall.jpg|Platinum print overall |
| − | File:Woman | + | File:Woman_Plat.print_det.jpg|Platinum print detail 1 |
| + | File:Woman.jpg|Platinum print detail 2 | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | ==Resources and Citations== | ||
| − | + | * A.Gottlieb "Chemistry and Conservation of Platinum and Palladium Photographs" ''JAIC'' 34:11-32, 1995. | |
* ''Caring for your Collections'', Arthur W Schulz (ed.), Harry N. Abrams, Inc. , New York, 1992 | * ''Caring for your Collections'', Arthur W Schulz (ed.), Harry N. Abrams, Inc. , New York, 1992 | ||
Latest revision as of 08:42, 26 July 2022
Description
A nonsilver photographic printing paper that used sodium or potassium tetrachloroplatinite as the light sensitive compound. Platinum was first used for photography in 1856 as an intensifier for silver prints. In 1873, William Willis patented the process for platinum printing in which paper is coated with a mixture of Oxalic acid and Potassium chloroplatinate. The Iron is reduced with exposure to light then oxidized with a Potassium oxalate developing solution with the concurrent reduction of fine-grain platinum. The prints are then fixed with a clearing solution containing Ammonium hydroxide Ammonium chloride, Oxalic acid, Sodium chloride, and Sodium hyposulfite. Platinum prints have a clear gray tonality, fine black details and a matte surface. They were discontinued by World War I due to the extremely high price of the metal.
Synonyms and Related Terms
platinotype; platinum print; potassium chloroplatinite paper
Additional Images
Resources and Citations
- A.Gottlieb "Chemistry and Conservation of Platinum and Palladium Photographs" JAIC 34:11-32, 1995.
- Caring for your Collections, Arthur W Schulz (ed.), Harry N. Abrams, Inc. , New York, 1992
- E.J.LaBarre, Dictionary and Encyclopedia of Paper and Paper-making, Swets & Zeitlinger, Amsterdam, 1969
- The Dictionary of Art, Grove's Dictionaries Inc., New York, 1996 Comment: "Photography"
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998