Difference between revisions of "Meteorite"
m (Text replace - "\[http:\/\/cameo\.mfa\.org\/materials\/fullrecord\.asp\?name=([^\s]+)\s(.*)\]" to "$2") |
|||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
meteorites; chondrite; tekite; aerolite; siderolite; siderite; australite; météorite (Fr.); meteorito (Esp., Port); Meteorit (Deut.); meteoriet (Ned.) | meteorites; chondrite; tekite; aerolite; siderolite; siderite; australite; météorite (Fr.); meteorito (Esp., Port); Meteorit (Deut.); meteoriet (Ned.) | ||
| − | == | + | == Resources and Citations == |
* R.F.Symmes, T.T.Harding, Paul Taylor, ''Rocks, Fossils and Gems'', DK Publishing, Inc., New York City, 1997 | * R.F.Symmes, T.T.Harding, Paul Taylor, ''Rocks, Fossils and Gems'', DK Publishing, Inc., New York City, 1997 | ||
| − | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "tektite" | + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "tektite" [Accessed October 11, 2002]. |
* ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | * ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
* Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | * Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | ||
| − | * | + | * Submission by Dr. Robert Ogilvie, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, August 2004. |
* ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | * ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | ||
Latest revision as of 15:09, 22 August 2020
Description
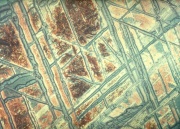
A mineral mass that falls to the earth from outer space. There are three main categories of meteorites: 1) stony (aerolites), which account for approximately 61% of all meteorites , 2) stony irons (siderolites) account for 20%, and 3) metallic or iron meteorites (siderite) make up about 15%. The stony meteorites are composed of silicates. Stony meteorites containing small spherical inclusions are called chondrites. Tekites (australite) are small, round, glassy stones that are thought to come from meteor impact with the earth. The stony irons are a combination of silicate stone cemented with metallic Iron. Iron meteorites contain iron alloyed with about 2-50% Nickel. They also contain small amounts of Cobalt, Arsenic, and Manganese. Meteoric iron has been used since ancient times for tools and weapons.
Synonyms and Related Terms
meteorites; chondrite; tekite; aerolite; siderolite; siderite; australite; météorite (Fr.); meteorito (Esp., Port); Meteorit (Deut.); meteoriet (Ned.)
Resources and Citations
- R.F.Symmes, T.T.Harding, Paul Taylor, Rocks, Fossils and Gems, DK Publishing, Inc., New York City, 1997
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "tektite" [Accessed October 11, 2002].
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- Submission by Dr. Robert Ogilvie, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, August 2004.
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998