Difference between revisions of "Amethyst"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:2006.630-SC179226.jpg|thumb|Watch brooch<br>MFA# 2006.630]] | [[File:2006.630-SC179226.jpg|thumb|Watch brooch<br>MFA# 2006.630]] | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | + | [[File:Amethyst.necklace.jpg|thumb|Amethyst necklace]] | |
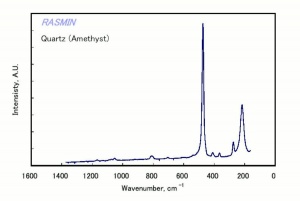
A clear, purple, [[quartz|quartz]] gemstone that has been gathered or mined since Neolithic times. Sources for amethysts include Germany (Idar-Oberstein, now delpleted), Ural Mountains, India, Sri Lanka, Egypt, Siberia, Brazil, Uruguay, Zambia (since early 1980s), Canada (Ontario, Nova Scotia), and the U.S.(Michigan, Virginia, Montana, Maine). The purple color of amethyst is due to trace impurities of [[iron|iron]] and [[manganese|manganese]]. Amethysts crystals are doubly refractive. The crystals are used for jewelry, pivot bearings in instruments, and recording needles. Oriental amethysts are purple [[corundum|corundum]]. Amethystine quartz is an amethyst streaked with bands of [[milky%20quartz|milky quartz]]. | A clear, purple, [[quartz|quartz]] gemstone that has been gathered or mined since Neolithic times. Sources for amethysts include Germany (Idar-Oberstein, now delpleted), Ural Mountains, India, Sri Lanka, Egypt, Siberia, Brazil, Uruguay, Zambia (since early 1980s), Canada (Ontario, Nova Scotia), and the U.S.(Michigan, Virginia, Montana, Maine). The purple color of amethyst is due to trace impurities of [[iron|iron]] and [[manganese|manganese]]. Amethysts crystals are doubly refractive. The crystals are used for jewelry, pivot bearings in instruments, and recording needles. Oriental amethysts are purple [[corundum|corundum]]. Amethystine quartz is an amethyst streaked with bands of [[milky%20quartz|milky quartz]]. | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:pa20703amethyst.jpg|thumb|amethyst]] |
| − | |||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| Line 34: | Line 33: | ||
| 1.544-1.553 | | 1.544-1.553 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
== Comparisons == | == Comparisons == | ||
Revision as of 12:09, 26 April 2022
Description
A clear, purple, Quartz gemstone that has been gathered or mined since Neolithic times. Sources for amethysts include Germany (Idar-Oberstein, now delpleted), Ural Mountains, India, Sri Lanka, Egypt, Siberia, Brazil, Uruguay, Zambia (since early 1980s), Canada (Ontario, Nova Scotia), and the U.S.(Michigan, Virginia, Montana, Maine). The purple color of amethyst is due to trace impurities of Iron and Manganese. Amethysts crystals are doubly refractive. The crystals are used for jewelry, pivot bearings in instruments, and recording needles. Oriental amethysts are purple Corundum. Amethystine quartz is an amethyst streaked with bands of Milky quartz.
Synonyms and Related Terms
quartz; amethystine quartz; Siberian amethyst (dark purple); rose-of France amethyst (pale purple to pink); Amethyst (Deut.); amatista (Esp.,); améthyste (Fr.); amethist (Ned.); ametyst (Pol.); ametista (Port.); ametist (Sven.)
Physical and Chemical Properties
Color=reddish purple in tungsten and bluish violet in daylight or fluorescent; Natural aquamarine is almost always color-banded; Turns to dull yellow/green with heat.
Trigonal crystal system. Low birefringence. Low thermal expansion.
Fracture = conchoidal. Luster = vitreous to greasy. Streak = white.
| Composition | SiO2 |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 7.0 |
| Density | 2.65-2.66 g/ml |
| Refractive Index | 1.544-1.553 |
Comparisons
Resources and Citations
- Mineralogy Database: Quartz
- Jack Odgen, Jewellery of the Ancient World, Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982
- A.Lucas, J.R.Harris, Ancient Egyptian Materials and Industries, Edward Arnold Publishers Ltd., London, 4th edition, 1962
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Yasukazu Suwa, Gemstones: Quality and Value, Volume 1, Sekai Bunka Publishing Inc., Tokyo, 1999 Comment: RI=1.544-1.553; Specific gravity=2.66;
- Michael O'Donoghue and Louise Joyner, Identification of Gemstones, Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2003 Comment: RI=1.544-1.553; Specific gravity=2.651; color=reddish purple in tungsten and bluish violet in daylight or fluorescent;
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amethyst
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 55
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979