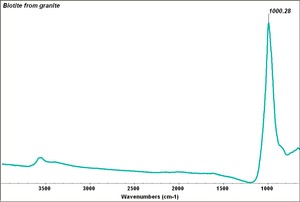
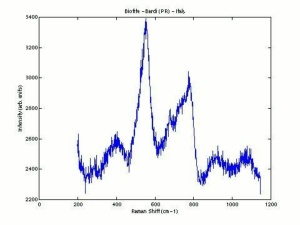
Biotite
Description
A common dark green, brown, or black mineral of the Mica group. Biotite is a silicate of Magnesium, Iron, Potassium, and Aluminum. It was named after the French physicist J.B. Biot. Biotite is found in granites, schists, and gneisses. It has been found in the lava of Vesuvius, Pikes Peak in Colorado, and Stone Mountain in Georgia, as well as many other locations. Biotite has a pearly luster and ranges from translucent to opaque. It cleaves into thin, somewhat elastic sheets.
Synonyms and Related Terms
iron mica; black mica; lepidomelane (rich in iron); Biotit (Deut.); biotita (Esp., Port.Br.); biotite (Fr., Port.); biotyt (Pol.); biotita (Port.); biotiet (Ned.)
Physical and Chemical Properties
Pleochroic (dark brown to yellow). High birefringence. Monoclinic tabular crystals. Cleavage = perfect in one direction. Luster = pearly to submetallic. Streak = colorless
| Composition | K2(Mg,Fe,Al)6(Si,Al)8O20(OH)4 |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 2.5 - 3.0 |
| Density | 2.7-3.4 |
Resources and Citations
- Mineralogy Database: Biotite
- Frank A. Lent, Trade names and Descriptions of Marbles, Limestones, Sandstones, Granites and Other Building Stones Quarried in the United States Canada and other Countries., Stone Publishing Co, New York, 1925
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "biotite" [Accessed December 11, 2001].
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 Comment: sp. gr. 2.8-3.4
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biotite (Accessed Sept. 2, 2005) hardness=2.5-3.0, spec. grav. = 2.7-3.1
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: density=2.7-3.1