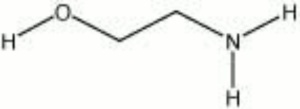
Monoethanolamine
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Description
A colorless, viscous liquid that is used commercially in many applications. Ethanolamines are used in nonionic detergents, and as solvents in dry cleaning. Ethanolamines are Hygroscopic and are used as humectants to soften hides and to condition Wool. Ethanolamines are used as corrosion inhibitors because they are an effective Scavenger for sulfur containing gases. The soaps of ethanolamines are used in shampoos, as surfactants and as emulsifiers. See also Diethanolamine, and Triethanolamine.
Synonyms and Related Terms
MEA; ethanolamine; colamine; 2-aminoethanol; 2-hydroxyethylamine
Risks
- Combustible. Flash point = 85C.
- Skin contact causes irritation and burns.
- Ingestion and inhalation are toxic.
- CISCO: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Miscible in water, methanol, acetone. A 10% solution has a pH of 9.
| Composition | HOCH2CH2NO2 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 141-43-5 |
| Melting Point | 10.3 C |
| Density | 1.0117 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 61.08 |
| Boiling Point | 170.8 C |
Resources and Citations
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 3772