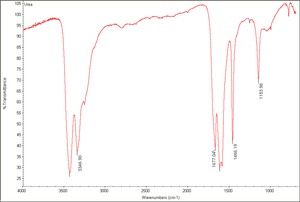
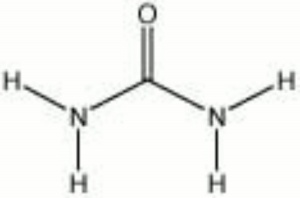
Urea
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Description
White, tetragonal prism shaped crystals with an ammonia odor. Urea was discovered in 1773 by Hilaire-Marin Rouelle as a constituent of Urine. It was first synthesized by Friedrich Wohler in 1828. Urea is used in the manufacture of fertilizers, plastics (polyurethanes), and flameproofing agents. It is also used as a viscosity modifier for Starch and Casein based paper coatings. Urea is also used by the paper industry to soften Cellulose. Urea rapidly denatures proteins.
Synonyms and Related Terms
carbamide; carbonyldiamide; urinstof (Dan.); Harnstoff (Deut.); urea(Esp., It., Sven.); urée (Fr.); ureum (Ned.); mocznik (Pol.); uréia (Port.)
Risks
- Noncombustible.
- ThermoFisher: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in water, ethanol, benzene. Slightly soluble in ether. Insoluble in chloroform.
| Composition | CO(NH2)2 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 57-13-6 |
| Melting Point | 132.7 C |
| Density | 1.335 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 60.06 |
Resources and Citations
- Palmy Weigle, Ancient Dyes for Modern Weavers, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York, 1974
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 10005
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 836
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Urea (Accessed Nov. 29, 2005) for language synonyms
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998