Difference between revisions of "Diatomaceous earth"
(username removed) |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
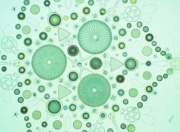
| − | An absorbent powder composed of the siliceous skeletons of microscopic water plants called diatoms. Diatomaceous earth is composed of 88% [ | + | An absorbent powder composed of the siliceous skeletons of microscopic water plants called diatoms. Diatomaceous earth is composed of 88% [[silica]]. The soft, whitish material is used as an inert [[pigment]] or [[filler]] in [[paper]], [[paint]], [[brick]], [[floor tile|floor tiles]], [[ceramic|ceramics]], [[linoleum]], [[plastic]], [[soap]], [[detergent]], and a large number of other products. It reduces [[gloss]], acts as a suspending agent, and increases viscosity. It absorbs dyes well and has been used as a base for lake colors. Diatomaceous earth is also used as an [[absorbent]], and [[poultice]] since it can absorb up to 4 times its weight of water. Because of its water-absorption capabilities, it is used as a desiccating [[insecticide]] and is often mixed in formulations with [[pyrethrins]]. Diatomaceous earth has also been used as a decolorizer and filtration aid for purifying [[oil|oils]], [[fat|fats]], and [[wax|waxes]]. Diatomaceous earth has replaced [[asbestos]] as an [[insulation]] for boilers, blast furnaces, because it is more resistant to shrinkage and does not fail at high temperatures. Other uses include [[sound insulation]] and as a very mild [[abrasive]] in metal [[polish (material)|polishes]] and toothpaste. |
[[File:diatomlargekes.jpg|thumb|Diatomaceous earth]] | [[File:diatomlargekes.jpg|thumb|Diatomaceous earth]] | ||
| + | |||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
Revision as of 14:39, 13 January 2014
Description
An absorbent powder composed of the siliceous skeletons of microscopic water plants called diatoms. Diatomaceous earth is composed of 88% Silica. The soft, whitish material is used as an inert Pigment or Filler in Paper, Paint, Brick, floor tiles, ceramics, Linoleum, Plastic, Soap, Detergent, and a large number of other products. It reduces Gloss, acts as a suspending agent, and increases viscosity. It absorbs dyes well and has been used as a base for lake colors. Diatomaceous earth is also used as an Absorbent, and Poultice since it can absorb up to 4 times its weight of water. Because of its water-absorption capabilities, it is used as a desiccating Insecticide and is often mixed in formulations with Pyrethrins. Diatomaceous earth has also been used as a decolorizer and filtration aid for purifying oils, fats, and waxes. Diatomaceous earth has replaced Asbestos as an Insulation for boilers, blast furnaces, because it is more resistant to shrinkage and does not fail at high temperatures. Other uses include Sound insulation and as a very mild Abrasive in metal polishes and toothpaste.
Synonyms and Related Terms
diatomite; poudre de diatomées (Fr.); tierra de diatomeas (Esp.); diatomito (Port.); Diatomeenerde, Kieselgur (Deut.); diatomeënaarde (Ned.); Celite® [Celite]; infusorial earth; kieselguhr; fossil flour; tripolite; Sil-O-Cel; diatomaceous silica; siliceous earth; Super-Cel; Kenite®; Diactiv®; Primisil®;
Other Properties
Soluble in alkalis. Insoluble in acids except HF.
| Density | 1.9-2.35 |
|---|---|
| Refractive Index | 1.435 |
Hazards and Safety
Inhalation of dust may cause silicosis. Noncombustible.
Comparisons
Properties of Common Abrasives
Authority
- The Dictionary of Paper, American Paper Institute, New York, Fourth Edition, 1980
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966 Comment: density 2.31 and ref.index.1.435
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p.266
- Reed Kay, The Painter's Guide To Studio Methods and Materials, Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1983
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- J. Dawson, 'Solving Museum Insect Problems: Chemical Control' , CCI Technical Bulletin, Candian Conservation Institute, Ottawa, No. 15
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000