Difference between revisions of "Polyvinyl chloride"
(username removed) |
|||
| (25 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File:L-SE 1057.1.2-SC186939.jpg|thumb| | + | [[File:L-SE 1057.1.2-SC186939.jpg|thumb|Bracelet by Peter Chang<br>MFA# 2017.4930]] |
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| + | [[File:63 polyvinylchl 200X.jpg|thumb|Polyvinyl chloride fiber,200x]] | ||
| + | [[File:63 polyvinylchl 200X pol.jpg|thumb|Polyvinyl chloride fiber, 200x polarized light]] | ||
| + | A thermoplastic polymer, made from the vinyl chloride monomer, that has a crystallinity range from 0 - ~ 10%. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) was discovered twice: in 1838, when French physicist Henri Regnault noticed a solid mass inside of a container of vinyl chloride gas, and in 1872, when German chemist Eugen Baumann observed the same phenomenon. PVC was patented in 1913 in Germany, but wasn’t commercialized until 1926, when a chemist working for the American company B. F. Goodrich, Waldo Semon, discovered a method to use PVC as a waterproof coating. The first moldable PVC, called Koroseal, was introduced in 1930. | ||
| − | + | PVC is resistant to moisture but stabilizers are needed to prevent discoloration from light and heat. Lightly plasticized PVC has been used for gramophone records. Heavily plasticized PVC is used as a rubber substitute for thin sheeting, wire coverings, gaskets, tubing, raincoats, storage sleeves and fabric coatings. Phthalate plasticizers were commonly used in the middle of the 20th century for PVC plastics. However, these oily plasticizers tended to creep and separate with time producing an oily surface and leaving a brittle substrate so some more recent PVC formulations use copolymerization techniques for film modification rather than plasticizers. Rigid unplasticized PVC was introduced in 1958 in Europe as alternative piping for town water services to replace corroded iron pipes. Artificial leathers, such as naugahyde (developed in 1936), became popular in the 1960s and 70s for use as upholstery. | |
| + | |||
| + | PVC is on the ILFI [[Red list of Materials|Red list]] of building materials. | ||
| − | |||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
PVC; vinyl; polyvinylchloride; poli(cloruro de vinilo) (Esp.); chlorure de polyvinyle (Fr.); polivinil cloruro (It.); policloreto de vinilo (Port.); poly(vinyl chloride); poly vinylchloride (sp); chloroethene polymer; vinyl chloride plastic; poly(chlorethylene) | PVC; vinyl; polyvinylchloride; poli(cloruro de vinilo) (Esp.); chlorure de polyvinyle (Fr.); polivinil cloruro (It.); policloreto de vinilo (Port.); poly(vinyl chloride); poly vinylchloride (sp); chloroethene polymer; vinyl chloride plastic; poly(chlorethylene) | ||
| − | Examples: Geon [B.F.Goodrich]; Koroseal [B.F.Goodrich]; Tygon; Vinagel; Elaston; Trovidur; Bexan [BX Plastics]; Bristrand [Polymers Inc.]; Pe-Ce-U [Bayer].; Tricovil; Kubo | + | Examples: Geon [B.F.Goodrich]; Koroseal [B.F.Goodrich]; [[Tygon]] (there are many types of Tygon, one of which is made from PVC); Vinagel; [[Vinylite]]; Elaston; Trovidur; Bexan [BX Plastics]; Bristrand [Polymers Inc.]; Pe-Ce-U [Bayer].; Tricovil; Kubo; Naugahyde; Duran; Duraleather; [[Fabrilite]]; Ultron |
| + | PVC boards: [[Komacel]] (Kommerling), [[Komatex]] (Kommerling), Celtec (Vycom), [[Forex]] (3A Composites), [[Sintra]] (3A Composites), Ex-cel FF (Jain Americas), PALIGHT (Palram), and ePVC (3A Composites) | ||
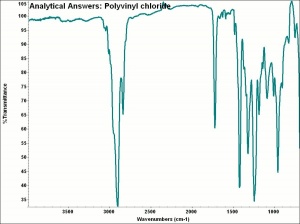
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|aaiPVC.jpg~FTIR]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|aaiPVC.jpg~FTIR]]] | ||
| − | == | + | == Applications == |
| − | + | Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is one of the most commonly manufactured plastics in the world, used in a wide variety of products including packaging, pipes, automotive parts, construction materials and furniture. | |
| − | + | == Personal Risks == | |
| − | + | If degraded, can transfer plasticizers, some of which are toxic. The vinyl chloride monomer is a suspected carcinogen. Vinyl chloride exposure is associated with an increased risk of a rare form of liver cancer (hepatic angiosarcoma), as well as brain and lung cancers, lymphoma, and leukemia. | |
| − | {| | + | FisherScientific :[https://fscimage.fishersci.com/msds/76785.htm SDS] |
| + | |||
| + | == Collection Risks == | ||
| + | Plasticizers and stabilizers may phase separate and ooze from polymer resulting in the formation of an oily film, white bloom on the surface of the material. This coating may corrode metal or transfer to objects nearby. The materials themselves may suffer discoloration, distortion, embrittlement and cracking. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Greg Smith and Michael Samide report that some rigid, unplasticized PVC construction boards give off a sulfur containing heat stabilizer (2-ethylhexyl thioglycolate [2-EHTG]) that can tarnish silver (publication forthcoming). However, they also reported finding several specific brands of PVC construction board, namely Komacel (Kommerling) and e-PVC (3A Composites) are safe for use in exhibition casework as they do not contain 2-EHTG. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Links to Oddy Test results posted on AIC Wiki Materials Database Pages for individual materials below'''<br> | ||
| + | See also pages for brand names of polyvinyl chloride based materials, such as [[Sintra®_Material|Sintra®]] | ||
| + | {| | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ° Foam [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0039 PVC] tested in 2016 <br> | ||
| + | | ° Sintra 3A [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0038 PVC] board tested in 2016 <br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ° Komatex [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0037 PVC] board tested in 2016 <br> | ||
| + | | ° Celtec 19 mm [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0036 PVC] foam board tested in 2015 <br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ° Celtec 12 mm [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0035 PVC] foam board tested in 2015 <br> | ||
| + | | ° Celtec [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0034 PVC] foam board tested in 2014 <br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ° Celtec or Sintra [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0033 PVC] foam board tested in 2014 <br> | ||
| + | | ° Freefoam [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0032 PVC] 10 mm foam board tested in December 2014 <br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ° Freefoam [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0031 PVC] 10 mm foam board tested in March-April 2014 <br> | ||
| + | | ° Freefoam [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0030 PVC] 10 mm foam board tested in October-November 2014 <br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ° Freefoam [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0029 PVC] 13 mm foam board tested in December 2014 <br> | ||
| + | | ° Freefoam [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0028 PVC] 13 mm foam board tested in March-April 2014 <br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ° Freefoam [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0027 PVC] 13 mm foam board tested in October-November 2014 <br> | ||
| + | | ° Palight foamed [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0026 PVC] sheet tested in 2014 <br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ° 5 mm white Forex [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0025 PVC] board tested in 2013 <br> | ||
| + | | ° 3 mm black Forex [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0024 PVC] board tested in 2013 <br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ° 3 mm blue Forex [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0023 PVC] board tested in 2013 <br> | ||
| + | | ° 3 mm dark blue Forex [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0022 PVC] board tested in 2013 <br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ° 3 mm dark yellow Forex [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0021 PVC] board tested in 2013 <br> | ||
| + | | ° 3 mm green Forex [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0020 PVC] board tested in 2013 <br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ° 3 mm grey Forex [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0019 PVC] board tested in 2013 <br> | ||
| + | | ° 3 mm orange Forex [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0018 PVC] board tested in 2013 <br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ° 3 mm red Forex [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0017 PVC] board tested in 2013 <br> | ||
| + | | ° 3 mm yellow Forex [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0016 PVC] board tested in 2013 <br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ° Foamalux [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0015 PVC] foam tested in 2013 <br> | ||
| + | | ° Excel Free Foam [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0014 PVC] board tested in 2013 <br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ° Excel Integral Foam [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0013 PVC] board tested in 2013 <br> | ||
| + | | ° Sintra [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0012 PVC] board tested in 2012 <br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ° Polyflex [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0011 PVC] with polyurethane coating tested in 2012 <br> | ||
| + | | ° Sintra white [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0010 PVC] board tested in 2012 <br> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | ° Sintra [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0009 PVC] board tested in 2012 <br> | |
| − | | [- | + | | ° Intecel [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0008 PVC] board tested in 2012 <br> |
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | ° Komacel [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0007 PVC] board tested in 2012 <br> | |
| − | | | + | | ° 6 mm Sintra [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0006 PVC] board tested in 2011 <br> |
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | ° [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0005 PVC] film tested in 2011 <br> | |
| − | | | + | | ° Foamalux [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0004 PVC] foam tested in 2010 <br> |
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | ° Laird Plastics expanded closed-cell [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0003 PVC] foam board tested in 2009 <br> | |
| − | | | + | | ° Forex Classic [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0002 PVC] board tested in 2009 <br> |
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | ° Clear Sav Self adhesive film with vinyl and [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#Polyvinyl_chloride0001 PVC] board tested in 2009 <br> | |
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | == Environmental Risks == |
| − | + | * Degrades with heat and light, first discoloring and becoming brittle, then producing hydrochloric acid gas. | |
| − | Degrades with heat and light | + | * If heated or burned, may form carbon monoxide or phosgene (carbonyl chloride). |
| + | * Production and incineration of PVC can introduce toxic chlorinated organic chemicals into the environment (e.g. dioxin). | ||
| + | * The [[Red list of Materials|Red List of Building Materials]] lists PVC and discourages it use. | ||
| − | + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | |
| − | + | * Soluble in chlorinated hydrocarbons and aromatic solvents. | |
| + | * Insoluble in water, alcohols, concentrated acids and alkalis. | ||
| + | * Burns with green, smoky flame and evolves HCl; it extinguishes when removed from flame source. | ||
| + | * readily degraded by ultraviolet light. | ||
| + | * Composition = [-H2CCHCl-]n | ||
| + | * CAS : 9002-86-2 | ||
| + | * Melting Point = 148 (dec) | ||
| + | * Density = 1.406 | ||
| + | * Refractive Index = 1.54 | ||
== Comparisons == | == Comparisons == | ||
| Line 53: | Line 121: | ||
[[media:download_file_363.pdf|Physical Properties for Selected Thermoplastic Resins]] | [[media:download_file_363.pdf|Physical Properties for Selected Thermoplastic Resins]] | ||
| − | + | == Resources and Citations == | |
| − | + | * Omnexus: [https://omnexus.specialchem.com/selection-guide/polyvinyl-chloride-pvc-plasticGuide on Polyvinyl chloride] | |
| − | == | + | * http://atozplastics.com/Upload/Literature/pvc.asp |
| − | + | * https://www.piper-plastics.com/2017/03/27/a-brief-history-of-pvc/ | |
| − | + | * Paul Wesley Brandt-Rauf, Yongliang Li, Changmin Long, Regina Monaco, Gopala Kovvali, and Marie-Jeanne Marion, "Plastics and carcinogenesis: The example of vinyl chloride", ''Journal of Carcinogenesis''. 2012; 11: 5. doi: 10.4103/1477-3163.93700 | |
| − | + | * Michael J.Samide, Gregory D. Smith, "Analysis and quantitation of volatile organic compounds emitted from plastics used in museum construction by evolved gas analysis–gas chromatography–mass spectrometry", ''Journal of Chromatography A'' Volume 1426, 24 December 2015, Pages 201-208 | |
| − | + | * https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/causes-prevention/risk/substances/vinyl-chloride | |
| − | + | * Contributions: Catherine Stephens, AIC Plastics Panel, 2020. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* Ralph Mayer, ''A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques'', Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing) | * Ralph Mayer, ''A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques'', Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing) | ||
| − | |||
* J.Gordon Cook, ''Handbook of Textile Fibres:II Man-made Fibres'', Merrow Publishing Co. , Durham, England Comment: p. 444; discovered by Henri Regnault in 1838 | * J.Gordon Cook, ''Handbook of Textile Fibres:II Man-made Fibres'', Merrow Publishing Co. , Durham, England Comment: p. 444; discovered by Henri Regnault in 1838 | ||
| − | |||
* M.Kaufman, ''The First Century of Plastics'', The Plastics and Rubber Institute, London, 1963 | * M.Kaufman, ''The First Century of Plastics'', The Plastics and Rubber Institute, London, 1963 | ||
| − | |||
* Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, ''Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology'', U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982 | * Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, ''Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology'', U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982 | ||
| − | |||
* ''Dictionary of Building Preservation'', Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996 | * ''Dictionary of Building Preservation'', Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996 | ||
| − | |||
* Pam Hatchfield, ''Pollutants in the Museum Environment'', Archetype Press, London, 2002 | * Pam Hatchfield, ''Pollutants in the Museum Environment'', Archetype Press, London, 2002 | ||
| − | |||
* Marjorie Shelley, ''The Care and Handling of Art Objects'', The Metropolitan Museum, New York, 1987 | * Marjorie Shelley, ''The Care and Handling of Art Objects'', The Metropolitan Museum, New York, 1987 | ||
| − | |||
* ''Caring for your Collections'', Arthur W Schulz (ed.), Harry N. Abrams, Inc. , New York, 1992 | * ''Caring for your Collections'', Arthur W Schulz (ed.), Harry N. Abrams, Inc. , New York, 1992 | ||
| − | |||
* Sharon Blank, An introduction to plastics and rubbers in collections, ''Studies in Conservation'', 35, 53-63, 1990 | * Sharon Blank, An introduction to plastics and rubbers in collections, ''Studies in Conservation'', 35, 53-63, 1990 | ||
| − | |||
* M. Baker, E. McManus, 'History, Care and Handling of America's Spacesuits', ''JAIC'', 31, 77-85, 1992 | * M. Baker, E. McManus, 'History, Care and Handling of America's Spacesuits', ''JAIC'', 31, 77-85, 1992 | ||
| − | |||
* Theodore J. Reinhart, 'Glossary of Terms', ''Engineered Plastics'', ASM International, 1988 | * Theodore J. Reinhart, 'Glossary of Terms', ''Engineered Plastics'', ASM International, 1988 | ||
| − | + | * Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, https://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000 | |
| − | * Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, | + | * History of Plastics: www.nswpmith.com.au/historyofplastics.html - discovered by Henri Regnault in 1838. |
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Revision as of 09:00, 6 November 2023
Description
A thermoplastic polymer, made from the vinyl chloride monomer, that has a crystallinity range from 0 - ~ 10%. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) was discovered twice: in 1838, when French physicist Henri Regnault noticed a solid mass inside of a container of vinyl chloride gas, and in 1872, when German chemist Eugen Baumann observed the same phenomenon. PVC was patented in 1913 in Germany, but wasn’t commercialized until 1926, when a chemist working for the American company B. F. Goodrich, Waldo Semon, discovered a method to use PVC as a waterproof coating. The first moldable PVC, called Koroseal, was introduced in 1930.
PVC is resistant to moisture but stabilizers are needed to prevent discoloration from light and heat. Lightly plasticized PVC has been used for gramophone records. Heavily plasticized PVC is used as a rubber substitute for thin sheeting, wire coverings, gaskets, tubing, raincoats, storage sleeves and fabric coatings. Phthalate plasticizers were commonly used in the middle of the 20th century for PVC plastics. However, these oily plasticizers tended to creep and separate with time producing an oily surface and leaving a brittle substrate so some more recent PVC formulations use copolymerization techniques for film modification rather than plasticizers. Rigid unplasticized PVC was introduced in 1958 in Europe as alternative piping for town water services to replace corroded iron pipes. Artificial leathers, such as naugahyde (developed in 1936), became popular in the 1960s and 70s for use as upholstery.
PVC is on the ILFI Red list of building materials.
Synonyms and Related Terms
PVC; vinyl; polyvinylchloride; poli(cloruro de vinilo) (Esp.); chlorure de polyvinyle (Fr.); polivinil cloruro (It.); policloreto de vinilo (Port.); poly(vinyl chloride); poly vinylchloride (sp); chloroethene polymer; vinyl chloride plastic; poly(chlorethylene)
Examples: Geon [B.F.Goodrich]; Koroseal [B.F.Goodrich]; Tygon (there are many types of Tygon, one of which is made from PVC); Vinagel; Vinylite; Elaston; Trovidur; Bexan [BX Plastics]; Bristrand [Polymers Inc.]; Pe-Ce-U [Bayer].; Tricovil; Kubo; Naugahyde; Duran; Duraleather; Fabrilite; Ultron
PVC boards: Komacel (Kommerling), Komatex (Kommerling), Celtec (Vycom), Forex (3A Composites), Sintra (3A Composites), Ex-cel FF (Jain Americas), PALIGHT (Palram), and ePVC (3A Composites)
Applications
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is one of the most commonly manufactured plastics in the world, used in a wide variety of products including packaging, pipes, automotive parts, construction materials and furniture.
Personal Risks
If degraded, can transfer plasticizers, some of which are toxic. The vinyl chloride monomer is a suspected carcinogen. Vinyl chloride exposure is associated with an increased risk of a rare form of liver cancer (hepatic angiosarcoma), as well as brain and lung cancers, lymphoma, and leukemia.
FisherScientific :SDS
Collection Risks
Plasticizers and stabilizers may phase separate and ooze from polymer resulting in the formation of an oily film, white bloom on the surface of the material. This coating may corrode metal or transfer to objects nearby. The materials themselves may suffer discoloration, distortion, embrittlement and cracking.
Greg Smith and Michael Samide report that some rigid, unplasticized PVC construction boards give off a sulfur containing heat stabilizer (2-ethylhexyl thioglycolate [2-EHTG]) that can tarnish silver (publication forthcoming). However, they also reported finding several specific brands of PVC construction board, namely Komacel (Kommerling) and e-PVC (3A Composites) are safe for use in exhibition casework as they do not contain 2-EHTG.
Links to Oddy Test results posted on AIC Wiki Materials Database Pages for individual materials below
See also pages for brand names of polyvinyl chloride based materials, such as Sintra®
| ° Foam PVC tested in 2016 |
° Sintra 3A PVC board tested in 2016 |
| ° Komatex PVC board tested in 2016 |
° Celtec 19 mm PVC foam board tested in 2015 |
| ° Celtec 12 mm PVC foam board tested in 2015 |
° Celtec PVC foam board tested in 2014 |
| ° Celtec or Sintra PVC foam board tested in 2014 |
° Freefoam PVC 10 mm foam board tested in December 2014 |
| ° Freefoam PVC 10 mm foam board tested in March-April 2014 |
° Freefoam PVC 10 mm foam board tested in October-November 2014 |
| ° Freefoam PVC 13 mm foam board tested in December 2014 |
° Freefoam PVC 13 mm foam board tested in March-April 2014 |
| ° Freefoam PVC 13 mm foam board tested in October-November 2014 |
° Palight foamed PVC sheet tested in 2014 |
| ° 5 mm white Forex PVC board tested in 2013 |
° 3 mm black Forex PVC board tested in 2013 |
| ° 3 mm blue Forex PVC board tested in 2013 |
° 3 mm dark blue Forex PVC board tested in 2013 |
| ° 3 mm dark yellow Forex PVC board tested in 2013 |
° 3 mm green Forex PVC board tested in 2013 |
| ° 3 mm grey Forex PVC board tested in 2013 |
° 3 mm orange Forex PVC board tested in 2013 |
| ° 3 mm red Forex PVC board tested in 2013 |
° 3 mm yellow Forex PVC board tested in 2013 |
| ° Foamalux PVC foam tested in 2013 |
° Excel Free Foam PVC board tested in 2013 |
| ° Excel Integral Foam PVC board tested in 2013 |
° Sintra PVC board tested in 2012 |
| ° Polyflex PVC with polyurethane coating tested in 2012 |
° Sintra white PVC board tested in 2012 |
| ° Sintra PVC board tested in 2012 |
° Intecel PVC board tested in 2012 |
| ° Komacel PVC board tested in 2012 |
° 6 mm Sintra PVC board tested in 2011 |
| ° PVC film tested in 2011 |
° Foamalux PVC foam tested in 2010 |
| ° Laird Plastics expanded closed-cell PVC foam board tested in 2009 |
° Forex Classic PVC board tested in 2009 |
| ° Clear Sav Self adhesive film with vinyl and PVC board tested in 2009 |
Environmental Risks
- Degrades with heat and light, first discoloring and becoming brittle, then producing hydrochloric acid gas.
- If heated or burned, may form carbon monoxide or phosgene (carbonyl chloride).
- Production and incineration of PVC can introduce toxic chlorinated organic chemicals into the environment (e.g. dioxin).
- The Red List of Building Materials lists PVC and discourages it use.
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Soluble in chlorinated hydrocarbons and aromatic solvents.
- Insoluble in water, alcohols, concentrated acids and alkalis.
- Burns with green, smoky flame and evolves HCl; it extinguishes when removed from flame source.
- readily degraded by ultraviolet light.
- Composition = [-H2CCHCl-]n
- CAS : 9002-86-2
- Melting Point = 148 (dec)
- Density = 1.406
- Refractive Index = 1.54
Comparisons
General Characteristics of Polymers
Physical Properties for Selected Thermoplastic Resins
Resources and Citations
- Omnexus: on Polyvinyl chloride
- http://atozplastics.com/Upload/Literature/pvc.asp
- https://www.piper-plastics.com/2017/03/27/a-brief-history-of-pvc/
- Paul Wesley Brandt-Rauf, Yongliang Li, Changmin Long, Regina Monaco, Gopala Kovvali, and Marie-Jeanne Marion, "Plastics and carcinogenesis: The example of vinyl chloride", Journal of Carcinogenesis. 2012; 11: 5. doi: 10.4103/1477-3163.93700
- Michael J.Samide, Gregory D. Smith, "Analysis and quantitation of volatile organic compounds emitted from plastics used in museum construction by evolved gas analysis–gas chromatography–mass spectrometry", Journal of Chromatography A Volume 1426, 24 December 2015, Pages 201-208
- https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/causes-prevention/risk/substances/vinyl-chloride
- Contributions: Catherine Stephens, AIC Plastics Panel, 2020.
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- J.Gordon Cook, Handbook of Textile Fibres:II Man-made Fibres, Merrow Publishing Co. , Durham, England Comment: p. 444; discovered by Henri Regnault in 1838
- M.Kaufman, The First Century of Plastics, The Plastics and Rubber Institute, London, 1963
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Dictionary of Building Preservation, Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996
- Pam Hatchfield, Pollutants in the Museum Environment, Archetype Press, London, 2002
- Marjorie Shelley, The Care and Handling of Art Objects, The Metropolitan Museum, New York, 1987
- Caring for your Collections, Arthur W Schulz (ed.), Harry N. Abrams, Inc. , New York, 1992
- Sharon Blank, An introduction to plastics and rubbers in collections, Studies in Conservation, 35, 53-63, 1990
- M. Baker, E. McManus, 'History, Care and Handling of America's Spacesuits', JAIC, 31, 77-85, 1992
- Theodore J. Reinhart, 'Glossary of Terms', Engineered Plastics, ASM International, 1988
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, https://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000
- History of Plastics: www.nswpmith.com.au/historyofplastics.html - discovered by Henri Regnault in 1838.