Difference between revisions of "Chalcedony"
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
[[File:Amulet 98697.jpg|thumb|Babylonian amulet<br>MFA# 98.697]] | [[File:Amulet 98697.jpg|thumb|Babylonian amulet<br>MFA# 98.697]] | ||
| − | A translucent, quartz stone with usually a waxy luster. Chalcedony has tiny microscopic crystals that are sometimes arranged in slender fibrous bands. [[agate|Agates]] are a banded variety of chalcedony. A glassy red chalcedony is known as [[carnelian]] or [[sard]]. A dull green variety colored with nickel oxide is called [[chrysoprase]]. Plasma is a bright emerald green chalcedony that is called [[bloodstone]] when it contains small red spots of [[jasper]]. Chalcedony has been mined or gathered since Paleolithic times. It was used as beads, amulets and seals and is still used as an ornamental stone and gemstone. The color and opacity can be changed by dyeing or heating. | + | A translucent, quartz stone with usually a waxy luster. Chalcedony has tiny microscopic crystals that are sometimes arranged in slender fibrous bands. [[agate|Agates]] are a banded variety of chalcedony. A glassy red to brown chalcedony is known as [[carnelian]] or [[sard]]. A dull green variety colored with nickel oxide is called [[chrysoprase]]. Plasma is a bright emerald green chalcedony that is called [[bloodstone]] when it contains small red spots of [[jasper]] or [[hematite]]. Chalcedony has been mined or gathered since Paleolithic times. It was used as beads, amulets and seals and is still used as an ornamental stone and gemstone. The color and opacity can be changed by dyeing or heating. |
[[File:Vespasian 98768.jpg|thumb|Roman Chalcedony bust<br>MFA# 98.768]] | [[File:Vespasian 98768.jpg|thumb|Roman Chalcedony bust<br>MFA# 98.768]] | ||
| + | |||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| Line 9: | Line 10: | ||
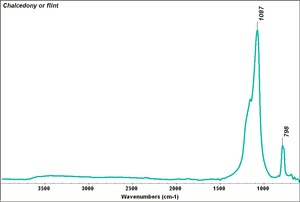
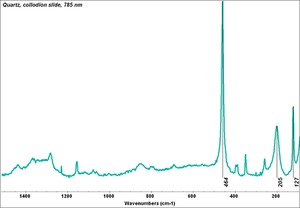
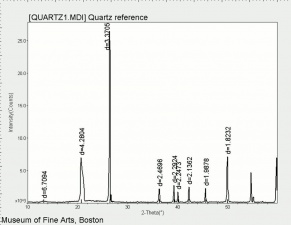
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|Chalcedony or flint.TIF~FTIR (MFA)|Quartz, collodion slide, 785 nm copy.tif~Raman (MFA)|QUARTZ1.jpg~XRD (MFA)]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Chalcedony or flint.TIF~FTIR (MFA)|Quartz, collodion slide, 785 nm copy.tif~Raman (MFA)|QUARTZ1.jpg~XRD (MFA)]]] | ||
| − | |||
== Physical and Chemical Properties == | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
* Streak = white | * Streak = white | ||
* Fluorescence = generally inert | * Fluorescence = generally inert | ||
| + | * Pleochroism = absent | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 30: | Line 31: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Refractive index | ! scope="row"| Refractive index | ||
| − | | 1.535 - | + | | 1.535 - 1.539 |
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row"| Birefringence | ||
| + | | undetectable to 0.004 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 47: | Line 51: | ||
* Gem Identification Lab Manual, Gemological Institute of America, 2016. | * Gem Identification Lab Manual, Gemological Institute of America, 2016. | ||
* Mineralogy Database: [http://www.webmineral.com/data/Quartz.shtml Quartz] | * Mineralogy Database: [http://www.webmineral.com/data/Quartz.shtml Quartz] | ||
| + | * Wikipedia: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chalcedony Chalcedony] {Accessed Dec 2022) | ||
* Jack Odgen, ''Jewellery of the Ancient World'', Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982 | * Jack Odgen, ''Jewellery of the Ancient World'', Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982 | ||
* ''Dictionary of Building Preservation'', Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996 | * ''Dictionary of Building Preservation'', Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996 | ||
| Line 53: | Line 58: | ||
* C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, ''Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals'', Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 | * C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, ''Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals'', Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 | ||
* Sue Fuller, ''Rocks and Minerals'', DK Publishing, Inc., New York City, 1995 | * Sue Fuller, ''Rocks and Minerals'', DK Publishing, Inc., New York City, 1995 | ||
| − | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "chalcedony" | + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "chalcedony" [Accessed December 4, 2001]. |
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 647 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 647 | ||
* Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | ||
Latest revision as of 10:39, 3 January 2023
Description
A translucent, quartz stone with usually a waxy luster. Chalcedony has tiny microscopic crystals that are sometimes arranged in slender fibrous bands. Agates are a banded variety of chalcedony. A glassy red to brown chalcedony is known as Carnelian or Sard. A dull green variety colored with nickel oxide is called Chrysoprase. Plasma is a bright emerald green chalcedony that is called Bloodstone when it contains small red spots of Jasper or Hematite. Chalcedony has been mined or gathered since Paleolithic times. It was used as beads, amulets and seals and is still used as an ornamental stone and gemstone. The color and opacity can be changed by dyeing or heating.
Synonyms and Related Terms
carnelian; sard; agate; chrysoprase; citrine; onyx; sardonyx; plasma; bloodstone; jasper; flint; plasma; Chalcedon (Deut.); calcedonia (Esp.); chalcédoine (Fr.); calcédoine (Fr.); chalcedon (Pol.); calcedônia (Port.); chalcedoon (Ned.)
Physical and Chemical Properties
- No visible crystals
- Fracture = conchoidal, uneven, splintery
- Luster = waxy to vitreous
- Streak = white
- Fluorescence = generally inert
- Pleochroism = absent
| Composition | SiO2 |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 6.5-7.0 |
| Density | 2.59-2.61 g/ml |
| Refractive index | 1.535 - 1.539 |
| Birefringence | undetectable to 0.004 |
Comparisons
Properties of Common Gemstones
Additional Images
Resources and Citations
- Gem Identification Lab Manual, Gemological Institute of America, 2016.
- Mineralogy Database: Quartz
- Wikipedia: Chalcedony {Accessed Dec 2022)
- Jack Odgen, Jewellery of the Ancient World, Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982
- Dictionary of Building Preservation, Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996
- Luciana and Tiziano Mannoni, Marble: the history of a culture, Facts on File Publications
- A.Lucas, J.R.Harris, Ancient Egyptian Materials and Industries, Edward Arnold Publishers Ltd., London, 4th edition, 1962
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Sue Fuller, Rocks and Minerals, DK Publishing, Inc., New York City, 1995
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "chalcedony" [Accessed December 4, 2001].
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 647
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998