Difference between revisions of "Triethanolamine"
m (Text replace - "\[http:\/\/cameo\.mfa\.org\/materials\/fullrecord\.asp\?name=([^\s]+)\s(.*)\]" to "$2") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|triethanolamine.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | |
A pale yellow, viscous liquid that lightly smells of [[ammonia%20%28anhydrous%29|ammonia]]. Triethanolamine is used as an [[emulsifier|emulsifier]] in [[nonionic%20detergent|nonionic detergents]], and as a [[solvent|solvent]] in dry cleaning. It dissolves dried paint films, [[fat|fats]], [[casein|casein]], [[shellac|shellac]], and [[wax|wax]]. Ethanolamines are [[hygroscopic|hygroscopic]] and are used as [[humectant|humectants]] to soften [[hide|hides]] and condition [[wool|wool]]. Ethanolamines are also used as corrosion inhibitors because they are an effective [[scavenger|scavenger]] for [[sulfur|sulfur]]-containing gases. Triethanolamine (TEA) is used in photographic developing baths to promote the formation of fine-grain structure. TEA is a strong base may be reacted with a non-water soluble organic materials, such as [[oleic%20acid|oleic acid]], to produce a water-soluble [[soap|soap]] for use as a cleaning agent, [[surfactant|surfactant]], and emulsifier. TEA soaps have been used to dissolve old, dried [[oil%20paint|oil paints]]. TEA is nonvolatile and highly reactive; it should be thoroughly removed from any surface after use. | A pale yellow, viscous liquid that lightly smells of [[ammonia%20%28anhydrous%29|ammonia]]. Triethanolamine is used as an [[emulsifier|emulsifier]] in [[nonionic%20detergent|nonionic detergents]], and as a [[solvent|solvent]] in dry cleaning. It dissolves dried paint films, [[fat|fats]], [[casein|casein]], [[shellac|shellac]], and [[wax|wax]]. Ethanolamines are [[hygroscopic|hygroscopic]] and are used as [[humectant|humectants]] to soften [[hide|hides]] and condition [[wool|wool]]. Ethanolamines are also used as corrosion inhibitors because they are an effective [[scavenger|scavenger]] for [[sulfur|sulfur]]-containing gases. Triethanolamine (TEA) is used in photographic developing baths to promote the formation of fine-grain structure. TEA is a strong base may be reacted with a non-water soluble organic materials, such as [[oleic%20acid|oleic acid]], to produce a water-soluble [[soap|soap]] for use as a cleaning agent, [[surfactant|surfactant]], and emulsifier. TEA soaps have been used to dissolve old, dried [[oil%20paint|oil paints]]. TEA is nonvolatile and highly reactive; it should be thoroughly removed from any surface after use. | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
TEA; tri(2-hydroxyethyl)amine; 2,2,2-triethanolamine; 2,2',2"-nitrilotrisethanol; tris(hydroxyethyl)amine; triethylolamine; trolamine | TEA; tri(2-hydroxyethyl)amine; 2,2,2-triethanolamine; 2,2',2"-nitrilotrisethanol; tris(hydroxyethyl)amine; triethylolamine; trolamine | ||
| − | + | == Risks == | |
| − | = | + | * Combustible. Flash point = 179 C. |
| + | * Skin irritant, strongly basic. | ||
| + | * Inhalation may be toxic. | ||
| + | * Cisco: [http://www.ciscochem.com/assets/triethanolamine-sds.pdf SDS] | ||
| − | + | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== | |
| − | Hygroscopic. Turns brown with exposure to air. | + | * Soluble in water, ethanol, acetone. Slightly soluble in ether. |
| + | * Hygroscopic. Turns brown with exposure to air. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 26: | Line 30: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | 21.2-21.6 | + | | 21.2-21.6 C |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 1.124 | + | | 1.124 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ||
| Line 35: | Line 39: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Boiling Point | ! scope="row"| Boiling Point | ||
| − | | 335.4 (dec) | + | | 335.4 C (dec) |
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | * ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | ||
Latest revision as of 12:11, 16 June 2022
Description
A pale yellow, viscous liquid that lightly smells of ammonia. Triethanolamine is used as an Emulsifier in nonionic detergents, and as a Solvent in dry cleaning. It dissolves dried paint films, fats, Casein, Shellac, and Wax. Ethanolamines are Hygroscopic and are used as humectants to soften hides and condition Wool. Ethanolamines are also used as corrosion inhibitors because they are an effective Scavenger for Sulfur-containing gases. Triethanolamine (TEA) is used in photographic developing baths to promote the formation of fine-grain structure. TEA is a strong base may be reacted with a non-water soluble organic materials, such as Oleic acid, to produce a water-soluble Soap for use as a cleaning agent, Surfactant, and emulsifier. TEA soaps have been used to dissolve old, dried oil paints. TEA is nonvolatile and highly reactive; it should be thoroughly removed from any surface after use.
See also Monoethanolamine, and Diethanolamine.
Synonyms and Related Terms
TEA; tri(2-hydroxyethyl)amine; 2,2,2-triethanolamine; 2,2',2"-nitrilotrisethanol; tris(hydroxyethyl)amine; triethylolamine; trolamine
Risks
- Combustible. Flash point = 179 C.
- Skin irritant, strongly basic.
- Inhalation may be toxic.
- Cisco: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Soluble in water, ethanol, acetone. Slightly soluble in ether.
- Hygroscopic. Turns brown with exposure to air.
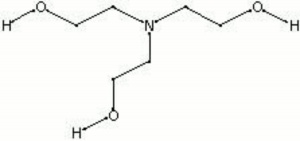
| Composition | N(CH2CH2OH)3 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 102-71-6 |
| Melting Point | 21.2-21.6 C |
| Density | 1.124 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 149.19 |
| Boiling Point | 335.4 C (dec) |
Resources and Citations
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 9798
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Hermann Kuhn, Conservation and Restoration of Works of Art and Antiquities, Butterworths, London, 1986
- Conservation Materials Ltd., Catalog