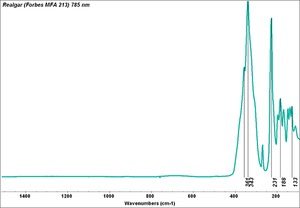
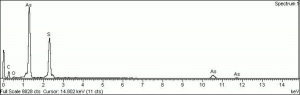
Arsenic disulfide
Description
A bright orange-red powder that occurs naturally as the mineral Realgar. Realgar is often found with lead and silver ores along with Orpiment (arsenic trisulfide). It was once widely used as a pigment because of its bright rich color, but perhaps less so than its mineral congener, orpiment. Early occurrences are known for works of art from China, India, Central Asia, and Egypt. In European painting, apart from fairly regular use in Venice in the 16th-century, the pigment occurs occasionally until about the middle of the 18th-century. It is a usual choice for the bright orange flowers depicted in Dutch 17th-century paintings, and enjoyed moderately regular use in British 17th- century and 18th-century painting, including as a pastel color. However, it is extremely toxic, which has had an effect on its range of application and availability. Realgar is not particularly stable and can undergo a transformation to a polymorph, Pararealgar, AsS; it can also deteriorate badly in oil paint films, resulting in rupturing, cracking and chalking, the pigment itself can fade under the action of light. Arsenic disulfide was also used to dehair and tan leathers, to kill rodents, and to print calico textiles. It is still used in fireworks to produce a bright blue fire and intense white light.
Synonyms and Related Terms
arsenic sulfide (legal name); Pigment Yellow 39; CI 77085; realgar (mineral); arsenic sulphide (Br.); realgar (Esp., It. Port.); disulfure d'arsenic (Fr.); solfuro d'arsenico (It.); red arsenic sulfide; red arsenic; ruby arsenic glass; arsenic monosulfide; red orpiment; burnt orpiment; ruby sulfur; roseaker; sandaraca
Risks
- Turns black in contact with copper and lead containing pigments.
- Highly toxic by inhalation and ingestion.
- Carcinogenic and mutagenic.
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Composition = As2S2 or AS2S4
- CAS = 56320-22-0
- Mohs Hardness = 1.5 - 2.0
- Melting Point = 307-320 C
- Density = 3.56-3.59 g/ml
- Refractive Index = 2.538, 2.684, 2.704
- Boiling Point = 565 C
- Soluble in alkaline sulfide solutions and nitric acid. Insoluble in water and hydrochloric acid.
- Monoclinic crystals, irregular; isotropic; pleochroic with high birefringence and straight extinction.
- Isotropic crystals with good cleavage in one direction.
- Fracture = conchoidal.
- Luster = resinous to adamantine.
- Streak = orange-yellow
- Burns with blue flame.
- Darkens with heat.
- Changes to red crystalline form at 170C.
Resources and Citations
- Wikipedia: Realgar Accessed Sept. 14, 2005 and August 2023
- Pigments Through the ages : Linnk
- Nicholas Eastaugh, Valentine Walsh, Tracey Chaplin, Ruth Siddall, Pigment Compendium, Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2004
- Ashok Roy, November 2007, submitted information.
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Susan E. Schur, Conservation Terminology: A review of Past & Current Nomenclature of Materials, Technology and Conservation, Spring (p.34-39); Summer (p.35-38); Fall (p.25-36), 1985
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 834
Record content reviewed by EU-Artech, November 2007.