Difference between revisions of "Pine"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:1990.483-SC3180.jpg|thumb|Yellow pine Wardrobe<br>MFA# 1990.483]] | [[File:1990.483-SC3180.jpg|thumb|Yellow pine Wardrobe<br>MFA# 1990.483]] | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | [[File:66.1132-SC35020.jpg|thumb|]] | + | [[File:66.1132-SC35020.jpg|thumb|Portative organ<br>MFA# 66.1132]] |
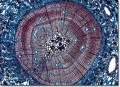
Any of several evergreen trees of the genus ''Pinus''. Pine trees are widely spread throughout the temperate regions of the northern hemisphere. They are fast growing and typical sizes for range from 15-45m. These evergreen trees have clustered needles (adult leaves) that can persist for 1.5-40 years. Cones can range in size froom 3-60 cm depending on species. Pine wood is soft, easy to work and has little shrinkage. It is moderately resistant to decay and insect attack. Common uses for the lumber are furniture, window frames, floors and roofing. The wood pulp is used to make kraft paper, paper board, and book paper. Pine trees have a resinous sap which is used to make turpentine and pine tar. Examples of pine trees are: [[Aleppo pine]], [[bristlecone pine]], [[Eastern white pine]], [[hoop pine]], [[jeffrey pine]], [[loblolly pine]], [[longleaf pine]], [[lodgepole pine]], [[pitch pine]], [[ponderosa pine]], [[monterey pine]], [[Scotch pine]], [[slash pine]], [[sugar pine]], [[shortleaf pine]], [[Western white pine]], and [[yellow pine]]. | Any of several evergreen trees of the genus ''Pinus''. Pine trees are widely spread throughout the temperate regions of the northern hemisphere. They are fast growing and typical sizes for range from 15-45m. These evergreen trees have clustered needles (adult leaves) that can persist for 1.5-40 years. Cones can range in size froom 3-60 cm depending on species. Pine wood is soft, easy to work and has little shrinkage. It is moderately resistant to decay and insect attack. Common uses for the lumber are furniture, window frames, floors and roofing. The wood pulp is used to make kraft paper, paper board, and book paper. Pine trees have a resinous sap which is used to make turpentine and pine tar. Examples of pine trees are: [[Aleppo pine]], [[bristlecone pine]], [[Eastern white pine]], [[hoop pine]], [[jeffrey pine]], [[loblolly pine]], [[longleaf pine]], [[lodgepole pine]], [[pitch pine]], [[ponderosa pine]], [[monterey pine]], [[Scotch pine]], [[slash pine]], [[sugar pine]], [[shortleaf pine]], [[Western white pine]], and [[yellow pine]]. | ||
* See also [[http://cameo.mfa.org/wiki/Category:Uemura_dye_archive '''Uemera Dye Archive''' (Kuromatsu)]] | * See also [[http://cameo.mfa.org/wiki/Category:Uemura_dye_archive '''Uemera Dye Archive''' (Kuromatsu)]] | ||
Revision as of 12:59, 5 October 2020
Description
Any of several evergreen trees of the genus Pinus. Pine trees are widely spread throughout the temperate regions of the northern hemisphere. They are fast growing and typical sizes for range from 15-45m. These evergreen trees have clustered needles (adult leaves) that can persist for 1.5-40 years. Cones can range in size froom 3-60 cm depending on species. Pine wood is soft, easy to work and has little shrinkage. It is moderately resistant to decay and insect attack. Common uses for the lumber are furniture, window frames, floors and roofing. The wood pulp is used to make kraft paper, paper board, and book paper. Pine trees have a resinous sap which is used to make turpentine and pine tar. Examples of pine trees are: Aleppo pine, Bristlecone pine, Eastern white pine, Hoop pine, Jeffrey pine, Loblolly pine, Longleaf pine, Lodgepole pine, Pitch pine, Ponderosa pine, Monterey pine, Scotch pine, Slash pine, Sugar pine, Shortleaf pine, Western white pine, and Yellow pine.
- See also [Uemera Dye Archive (Kuromatsu)]
Synonyms and Related Terms
Pinus; fyr-slægten (Dan.); Kiefern (Deut.); Föhren (Deut.); pino (Esp., It.); pin (Fr.); den (Ned.); furu (Nor.); sosna (Pol.); pinho (Port.); tallar (Sven.); matsu (Jap.)
Physical and Chemical Properties
Yellow powdery pollen is released in the spring or early summer. Density = 25-35 ppcf
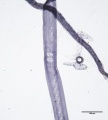
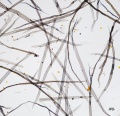
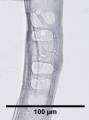
Paper fiber type: Softwood. Using transmitted light microscopy, pine fibers are identified by the presence of pinoid or fenestriform pits. Hard pines can be distinguished by the presence of dentate ray tracheids. See individual species for specific morphological characteristics. Appearance with Graff "C" stain: varies with pulping and bleaching. Average dimensions of fibers: varies by species. Common pulping method: kraft and sulfite.
Additional Images
Resources and Citation
- Schoch, W., Heller, I., Schweingruber, F.H., Kienast, F., 2004:Wood anatomy of central European Species: Common Pine,Scots Pine, Pinus silvestris L.
- F. H. Titmuss, Commercial Timbers of the World, The Technical Press Ltd., London, 1965
- Dictionary of Building Preservation, Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "Pine." Accessed: 14 July 2004
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pine (Accessed Nov. 9, 2005)
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 612
- Museum of Japanese Traditional Art Crafts at http://www.nihon-kogeikai.com/ (Jap. term)
- Marja-Sisko Ilvessalo-Pfäffli. Fiber Atlas: Identification of Papermaking Fibers (Springer Series in Wood Science). Springer, 1995.
- Walter Rantanen. "Fiber ID Course." Integrated Paper Services. June 2013. Lecture.