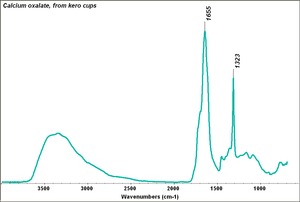
Calcium oxalate
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Description
White, crystalline powder that occurs naturally as the minerals Whewellite and Weddellite. Calcium oxalate also occurs in some plants such as dumb cane, rhubarb and spinach. The powdered mineral is used in ceramic glazes. Calcium oxalate forms naturally on the surface of weathered calcareous stones due to reaction of Oxalic acid excretions from some types of Lichen and fungi. Since calcium oxalate is less soluble than Calcium carbonate in acids, the production of thin films of calcium oxalate has been investigated as a protective surface treatment for Limestone (Cezar 1998).
Synonyms and Related Terms
whewellite; weddellite; ethanedioic acid calcium salt
Risks
- Contact may cause irritation.
- Ingestion is harmful.
- Fisher Scientific: MSDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in dilute mineral acids. Insoluble in water, acetic acid. Slightly hygroscopic.
| Composition | CaC2O4 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 5794-28-5 |
| Melting Point | 200 C |
| Density | 2.2 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 128.1 |
Resources and Citations
- T.M. Cezar, "Calcium Oxalate: A Surface Treatment for Limestone" Journal of Museum Studies, No. 4, May 1988: http://www.jcms.ucl.ac.uk/issue4/cezar.html
- M. del Monte, C. Sabbioni, G.Zappia. The origin of calcium oxalates on historical buildings, monuments and natural outcrops. The science of the total environment 67, (1987), pp. 17-39
- B. Ford, I.MacLeod, P.Haydock, "Rock art pigments from Kimberley region of Western Australia: identification of the minerals and conversion mechanisms." Studies in conservation 39, no. 1 (1994), pp. 57-69
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 1732
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calcium_oxalate (Accessed Sept 2 2005)