Difference between revisions of "Protein"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(username removed) |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | Proteins are natural polymers composed of chains of [ | + | Proteins are natural polymers composed of chains of [[amino%20acid|amino acids]] connected by peptide linkages. Proteins occur in the cells of all living organisms and in biological fluids. Their primary structure is determined by the order of their amino acids. Examples of soluble proteins include [[enzyme|enzymes]] and antibodies. Insoluble proteins include [[keratin|keratin]] and [[collagen|collagen]]. Examples of protein containing compounds are [[leather|leather]], [[gelatin|gelatin]], [[albumen|albumen]], [[animal%20glue|animal glue]], [[silk|silk]], [[ivory|ivory]], [[egg|egg]], and [[casein|casein]]. |
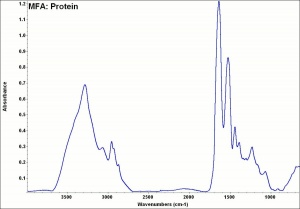
| − | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|MFA- Protein.jpg~FTIR]]] | |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | natural polyamide; ivory; zein; blood; animal glue; leather; silk; protein (Dan., Sven.); Proteine (Deut.); proteina (Esp.); | + | natural polyamide; ivory; zein; blood; animal glue; leather; silk; protein (Dan., Sven.); Proteine (Deut.); proteina (Esp.); protéine (Fr.); proteine (It.); proteïne (Ned.); białko (Pol.); |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | |
| − | Fluorescent detection agents: [ | + | * Autofluorescence color is pale white to pale yellow |
| + | * Non-fluorescent detection agents: [[amido%20black|amido black]], [[Brilliant%20Blue%20R-250|Brilliant Blue R-250]], [[Ponceau%20S|Ponceau S]], [[resorcinol%20blue|resorcinol blue]] | ||
| + | * Fluorescent detection agents: [[Blancophor%20R|Blancophor R]], [[dansyl%20chloride|dansyl chloride]], [[fluorescamine|fluorescamine]], [[Fluorescein%20isothiocyanate%20|Fluorescein isothiocyanate]] (FITC), [[Lissamine%20Rhodamine%20B%20Sulfonyl%20Chloride|Lissamine Rhodamine B Sulfonyl Chloride]] (LISSA), [[tetramethyl%20rhodamine%20isothiocyanate|tetramethyl rhodamine isothiocyanate]] (TRITC); [[Texas Red|Texas Red®]]; [[cycloheptaamylose%20dansyl%20chloride|cycloheptaamylose dansyl chloride]] (DC-C7A) | ||
| − | == | + | == Resources and Citation == |
| − | * | + | * R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, ''Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia'', Dover Publications, New York, 1966 |
| − | * | + | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 637 |
| − | * | + | * Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 |
| − | * | + | * John S. Mills, Raymond White, ''The Organic Chemistry of Museum Objects'', Butterworth Heineman, London, 2nd ed., 1994 |
* ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | * ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | ||
| − | * Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, | + | * Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, https://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000 |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:59, 22 October 2022
Description
Proteins are natural polymers composed of chains of amino acids connected by peptide linkages. Proteins occur in the cells of all living organisms and in biological fluids. Their primary structure is determined by the order of their amino acids. Examples of soluble proteins include enzymes and antibodies. Insoluble proteins include Keratin and Collagen. Examples of protein containing compounds are Leather, Gelatin, Albumen, Animal glue, Silk, Ivory, Egg, and Casein.
Synonyms and Related Terms
natural polyamide; ivory; zein; blood; animal glue; leather; silk; protein (Dan., Sven.); Proteine (Deut.); proteina (Esp.); protéine (Fr.); proteine (It.); proteïne (Ned.); białko (Pol.);
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Autofluorescence color is pale white to pale yellow
- Non-fluorescent detection agents: Amido black, Brilliant Blue R-250, Ponceau S, Resorcinol blue
- Fluorescent detection agents: Blancophor R, Dansyl chloride, Fluorescamine, Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC), Lissamine Rhodamine B Sulfonyl Chloride (LISSA), Tetramethyl rhodamine isothiocyanate (TRITC); Texas Red®; Cycloheptaamylose dansyl chloride (DC-C7A)
Resources and Citation
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 637
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- John S. Mills, Raymond White, The Organic Chemistry of Museum Objects, Butterworth Heineman, London, 2nd ed., 1994
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, https://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000